【IT168 专稿】当我们希望获得一个表中符合条件的记录的行数时,一般借助于T-SQL函数count(*)来实现。不过,如果你的表中包含了数百万条记录,返回整个表的记录数可能需要花费较长时间,会导致查询性能非常低。
1.Count()函数
DBA们都知道如何使用count(*)函数,也知道它对性能的影响。SQL Server需要进行一次完整的索引/表扫描,才能返回表的记录总数。建议DBA不要针对这个表使用聚合函数count(),因为它会影响数据库的性能。 接下来我们在示例数据库AdventureWorkstation的查询分析器中执行以下查询语句:
go
select count (*) from Sales.SalesOrderDetail
查询分析器返回的结果为121317行。
当我们点击SQL Server 2005 Management Studio工具栏中的“显示预计的执行计划”图标时,我们可以看到如下图示:
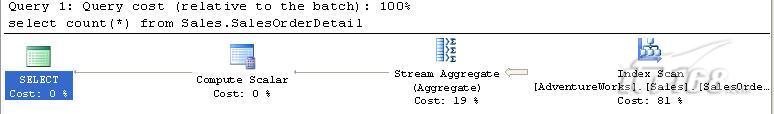
图1 查看count(*)执行计划
如上图所示,该函数执行过程中将从右至左执行如下操作:
•对整个表进行索引扫描,这是一个相当耗时的过程。
•接下来执行流聚合。
2.新方法row_count()
在SQL Server 2005的对象目录视图(Object Catalog Views)包含如下信息:sys.partitions和sys.allocation_units被用来获得整个表的记录总数。这个函数可以在SQL Server 2005中使用。
sys.partitions视图
sys.partitions视图包含了数据库中所有表和索引的每个分区在表中对应的每一行。即使SQL Server 2005中的所有表和索引并未显式分区,也至少在这个视图中包含一个分区。
该视图包含如下字段,它们将被用于这个新方法:
|
字段名称
|
数据类型
|
描述
|
|
partition_id
|
bigint
|
分区的ID,它在一个数据库中是唯一的。
|
|
object_id
|
int
|
分区所属表的ID。每个表至少包含一个分区。
|
|
index_id
|
int
|
分区所属对象内索引的ID。
0:heap表
1:具有集群索引
|
|
rows
|
bigint
|
分区中表的行数。
|
sys.allocation_units视图
sys.allocation_units视图包含了数据库中的每个分配单元在表中的每一行。
该视图中可以被新方法使用的字段如下:
|
字段名称
|
数据类型
|
描述
|
|
container_id
|
bigint
|
container_id=sys.partitions.partition_id
|
|
Type
|
tinyint
|
0 = 已删除
1 = 行内数据(除LOB之外的所有数据类型)
2 = 大型对象(LOB)数据(text、ntext、 image、xml)
3 = 行溢出数据
|
在这个新用户自定义函数row_count中,[sys.partitions]视图与[sys.allocation_units]视图是相关联的。过滤器的选择基于如下标准:
Drop FUNCTION [dbo].[row_count]
GO
Create FUNCTION dbo.row_count (@table_name sysname)
— @table_name we want to get count
RETURNS bigint
/*
——————————————————-
— Function Name: row_count
— Author: Mohamed Hassan
— Email: moh_hassan20@yahoo.com
— Development Date: 08/11/2008
— Version: 1.0
— Description: Return row count of the whole table, as a replacement for count(*) , give extra performance at least 70% over , than count(*) for large tables with millions of rows
— SQL Server: SQL server 2005
— Usage Example: select dbo.row_count ('Sales.SalesOrderDetail')
— Copyright:
This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as
published by the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the
License, or any later version.
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
——————————————————-
*/
AS
BEGIN
DECLARE @nn bigint — number of rows
IF @table_name IS NOT NULL
BEGIN
Select @nn = sum( p.rows )
FROM sys.partitions p
LEFT JOIN sys.allocation_units a ON p.partition_id = a.container_id
Where
p.index_id in(0,1) — 0 heap table , 1 table with clustered index
and p.rows is not null
and a.type = 1 — row-data only , not LOB
and p.object_id = object_id(@table_name)
END
RETURN (@nn)
END
GO
函数用法
 use AdventureWorks
use AdventureWorks2
 go
go3
 select dbo.row_count ('Sales.SalesOrderDetail')
select dbo.row_count ('Sales.SalesOrderDetail')在查询分析器中,上述语句返回的结果为12317行,与前面使用count(*)返回的结果一致,但是其执行速度更快,性能更高。
例2:
dbo.row_count(TABLE_SCHEMA +'.'+TABLE_NAME) rows
FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES
where TABLE_TYPE ='BASE TABLE'
ORDER BY rows desc
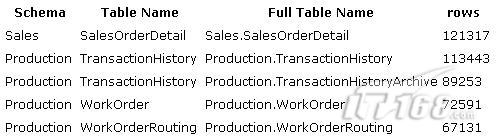
表1
go
select count (*) from Sales.SalesOrderDetail
go
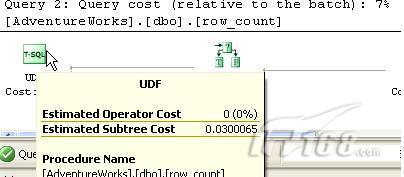
图2

图3
 Mikel
Mikel

