
转载:http://www.cnblogs.com/baihmpgy/archive/2009/09/16/1567387.html
以下是界面类似我们正在开发的一个产品的主界面,前端展示采用Flex开发,后端系统是基于Java的SOA框架。界面左边是导航条,右边是内容区(当然 还有其它栏目,在此忽略)。内容区一般由多个UI Part组成,每一个Part利用异步机制从后端获取数据,此外,它还将接收来自后端的通知消息。整个界面非常符合微软CAB思想,不过Flex没有 CAB组建,但是可以采用Microsoft用户控件方式定义一块一块内容。界面内容区的UI Part可能会被重用。
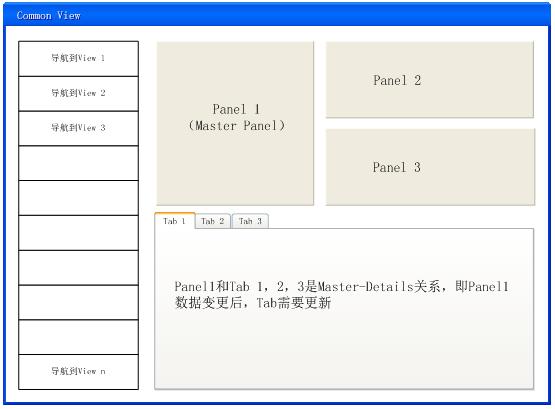
在 设计中,我想利用界面组合思想来设计,采用该思想的优点有:1)界面分割成不同的组成部分,每一部分实现一个功能,更加符合SRP原则;2)实现每一个 UI Part时,只需专注复杂界面中的一块内容的实现,比较简单;3)容易实现重用;其缺点有:1)每一个界面由多个UI Part组成,需要维护UI Part之间的联系;2)新手不太容易看懂界面的实现。
鉴于微软界面组合诸多优点,我决定将其思想引入到Flex,自己实现一个Composition SDK based on Flex,该SDK实现过程中参考了CAB & SCSF和Prism。
考虑到该软件需要实现的功能,这个SDK将支持如下功能:
1 UI Part生命周期管理。每一个UI Part在显示的时候,需要从后端获取数据,然后监听数据更新消息,当点击界面的“Tab 2”时,Tab 1被隐藏并停止监听消息,Tab 2被显示。在我看来每一个UI Part具有Activated、Deactivated和Closed生命周期状态,当处于Activated状态时,UI Part显示呈现所需数据,当处于Deactivated状态时,UI Part被隐藏并停止更新数据,当处于Closed状态时,UI Part被关闭并停止更新数据,它将被销毁。生命周期管理功能提出的目的是为了实现生命周期变更驱动数据更新,也就是每一个组件数据更新是由其自身的生命 周期状态决定的,不需要由父节点控制,从而实现更大粒度复用。
2 UI Part组合和动态注入。这个功能允许直接在视图容器类中定义每一个UI Part,在这种方式中,一旦容器被显示,则所有的UI Part将被显示;或者是其中某些UI Part是在运行时被动态注入并呈现的,当容器呈现时,根据需要注入特定的UI Part。
3 Master-Details UI Part支持。Master-Details UI Part是一对特殊的UI Part,当Master UI Part的数据发生变更后,Details UI Part也需要更新,和.NET的Master-Details View是一样的。
4 采用Hook机制实现,使得在实现1~3功能的时候,可以尽量与标准控件兼容,不必创建自定义控件或者仅需创建非常简单的自定义控件。Hook机制原理如 下:A)每一个功能由一个Hook实现;B)比如LifecycleHook,对于一个叶子节点的组件,当其被显示/隐藏/关闭时,该Hook要维护其状 态;对于一个容器节点,它除了要维护自己的状态,还要维护子控件的状态,比如VBox容器,当VBox被显示时,其状态为Activated且其所有一级 子节点状态也是Activated;而对于TabNavigator容器,当其被显示时,其状态为Activated且当前选中的Tab的状态也是 Activated,其余Tab的状态都是Deactivated;C)Hook的创建过程是递归的监听界面根节点 onChildAdded/Removed事件;D)SDK提供Hook注册表和Hook管理器,Hook注册表定义了每一类型的组件对应的Hook,而 Hook管理器定义了每一个控件对应的Hook实例。
5 基于该SDK,每一个视图的设计由Workspace和UI Part组成,Workspace使用Flex标准容器控件定义了界面的布局;UI Part是界面每一部分功能的实现,自己封装了生命周期驱动的数据更新。
代码的设计比较简单,其结构如下:
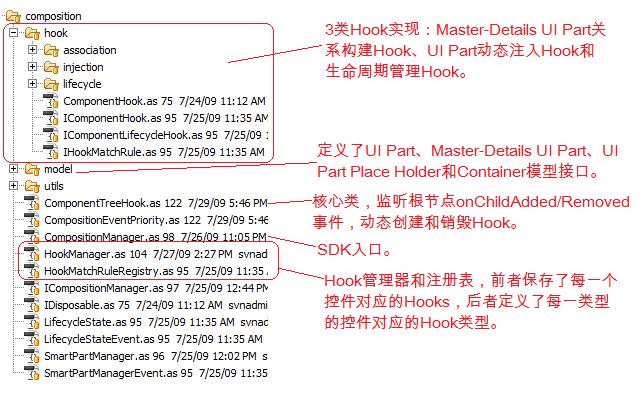
ComponentTreeHook是整个Hook机制的核心类,它将递归监听根节点控件的onChildAdded/Removed,当有子节点添加时,递归挂载整个控件树,挂载过程代码如下:

 Code
Code
1 /**
2 * Create the hooks for current component tree and listen the CHILD_ADD/CHILD_REMOVE
3 * events of each component.
4 *
5 * @param comp The root component of the component tree.
6 *
7 */
8 override public function hook(comp:UIComponent):void
9 {
10 if(!isHooked)
11 {
12 super.hook(comp);
13 hookComponentTree(component);
14 }
15 }
16
17 private function hookComponentTree(comp:UIComponent):void
18 {
19 doComponentTreeHooking(comp, true, hookComponentNode);
20 }
21
22 /**
23 * Do the hooking for a component tree.
24 * @param comp The root component.
25 * @param hookComponentFunc The actual hook function.
26 *
27 */
28 private function doComponentTreeHooking(comp : UIComponent, hooked : Boolean, hookComponentFunc : Function) : void
29 {
30 if(!comp)
31 {
32 return;
33 }
34
35 // Hook the node from top to bottom.
36 var queue : Array = [ comp ];
37 var tempComp : UIComponent = null;
38 var tempContainer : Container = null;
39 var tempContainerChildren : Array;
40 while(queue.length > 0)
41 {
42 // Get a component from queue.
43 tempComp = queue.shift() as UIComponent;
44 if(!tempComp)
45 {
46 continue;
47 }
48
49 // Do the hook for this component.
50 hookComponentFunc(tempComp);
51
52 // Get the children of current component and push them to queue.
53 tempContainer = tempComp as Container;
54 // SmartPart here is treast as a Component.
55 if(tempContainer && !(tempContainer is ISmartPart))
56 {
57 if(hooked)
58 {
59 tempContainer.addEventListener(ChildExistenceChangedEvent.CHILD_ADD, onChildAdded, false, CompositionEventPriority.Create_HOOK);
60 tempContainer.addEventListener(ChildExistenceChangedEvent.CHILD_REMOVE, onChildRemoved, false, CompositionEventPriority.DESTORY_HOOK);
61 }
62 else
63 {
64 tempContainer.removeEventListener(ChildExistenceChangedEvent.CHILD_ADD, onChildAdded);
65 tempContainer.removeEventListener(ChildExistenceChangedEvent.CHILD_REMOVE, onChildRemoved);
66 }
67 tempContainerChildren = tempContainer.getChildren();
68 for each(var child : UIComponent in tempContainerChildren)
69 {
70 queue.push(child);
71 }
72 }
73 }
74 }附件是该SDK的测试文件,包含UI测试和Unit测试。测试文件


 Mikel
Mikel

