来源: SqlServer性能优化 查询和索引优化(十二) – 孙丽媛 – 博客园
查询优化的过程:
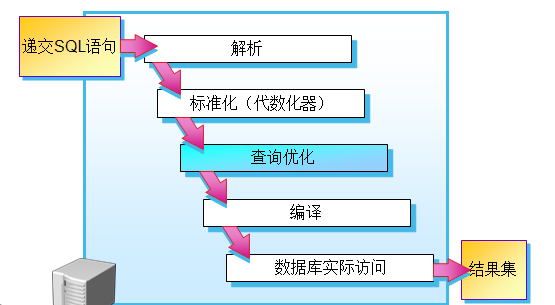
查询优化:
功能:分析语句后最终生成执行计划
分析:获取操作语句参数
索引选择
Join算法选择
创建测试的表:
|
1
|
select * into EmployeeOp from AdventureWorks2014.HumanResources.Employee |
建立非聚集索引:
|
1
|
create nonclustered index nc_employee_vacationhours on employeeop(vacationhours) |
执行语句:
|
1
|
select LoginID,JobTitle,VacationHours,SickLeaveHours from EmployeeOp where VacationHours>40 --table scan>10% |

执行语句:
|
1
|
select LoginID,JobTitle,VacationHours,SickLeaveHours from EmployeeOp where VacationHours>99 --nonclustered index |
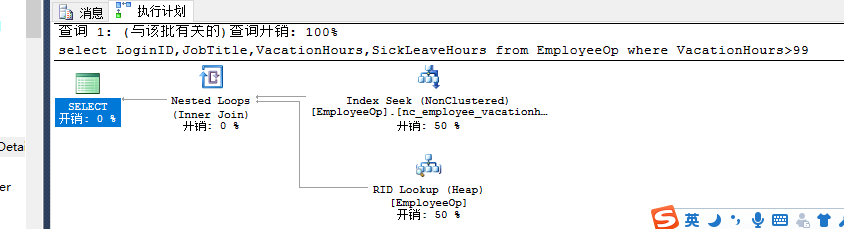
查询结果集的数据范围影响对索引的选择。
两个查询条件:
|
1
2
|
select LoginID,JobTitle,VacationHours,SickLeaveHours from EmployeeOp where VacationHours>40and SickLeaveHours>60--scan |
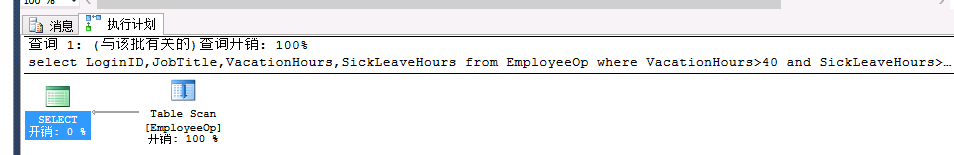
SQLServer 的查询结果集会认为用哪个列查询的结果少,就选择哪个。在去and 的第二个结果,最终返回结果集。
|
1
2
|
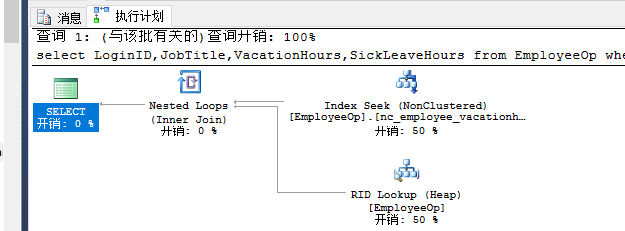
select LoginID,JobTitle,VacationHours,SickLeaveHours from EmployeeOp where VacationHours>99and SickLeaveHours>60--nonclustered index nc_employee_vacationhours |
单独选择:
|
1
|
select LoginID,JobTitle,VacationHours,SickLeaveHours from EmployeeOp where SickLeaveHours>60--table scan |
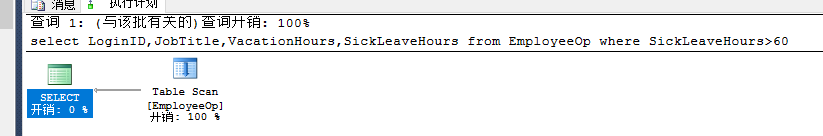
创建非聚集索引:
|
1
|
create nonclustered index nc_employee_sickleavehours on EmployeeOp(SickLeaveHours) |
执行:
|
1
|
select LoginID,JobTitle,VacationHours,SickLeaveHours from EmployeeOp where SickLeaveHours>60--table scan |
执行:
|
1
|
select LoginID,JobTitle,VacationHours,SickLeaveHours from EmployeeOp where SickLeaveHours>88--nc_employee_sickleavehours |
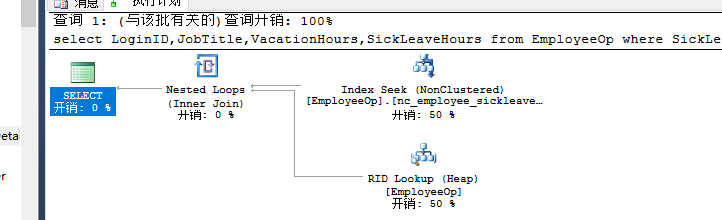
执行:
|
1
2
|
select LoginID,JobTitle,VacationHours,SickLeaveHours from EmployeeOp where VacationHours>99and SickLeaveHours>88--nonclustered index nc_employee_vacationhours |
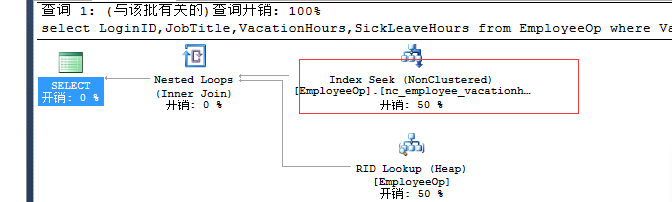
在两列上做一个索引:
|
1
|
create nonclustered index nc_employee_vacationsickleavehours on EmployeeOp(VacationHours,SickLeaveHours) |
执行语句:(使用了符合索引)
|
1
2
|
select LoginID,JobTitle,VacationHours,SickLeaveHours from EmployeeOp where VacationHours>99and SickLeaveHours>88-- nc_employee_vacationsickleavehours |
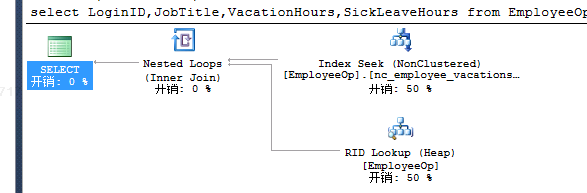
执行:(随机)
|
1
|
select LoginID,JobTitle,VacationHours,SickLeaveHours from EmployeeOp where VacationHours>99<br>--nc_employee_vacationhours nc_employee_vacationsickleavehours |
执行:
|
1
2
|
select LoginID,JobTitle,VacationHours,SickLeaveHours from EmployeeOp where SickLeaveHours>88--nc_employee_sickleavehours |
执行:
|
1
|
select * from EmployeeOp where SickLeaveHours>88 --nc_employee_sickleavehours |
创建聚集索引:
|
1
|
create clustered index c_Employee_BusinessEntityID on EmployeeOp(BusinessEntityID) |
执行:
|
1
|
select * from EmployeeOp where SickLeaveHours>88 --nc_employee_sickleavehours key连 c_ID聚集索引 |
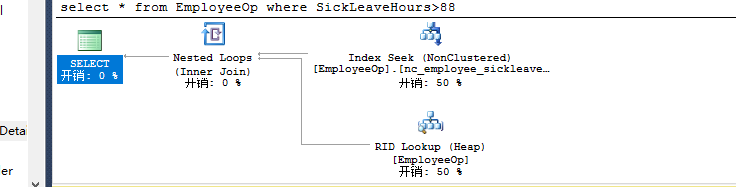
建立include索引:
|
1
2
|
create nonclustered index nc_employee_vacationsickleavehoursinclude on EmployeeOp(VacationHours,SickLeaveHours) include(LoginID,JobTitle) |
执行:
|
1
2
|
select LoginID,JobTitle,VacationHours,SickLeaveHours from EmployeeOp where VacationHours>99and SickLeaveHours>88 --nc_employee_vacationsickleavehoursinclude |
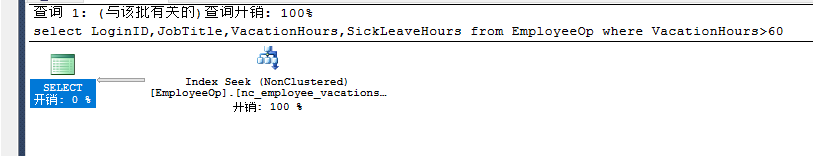
执行:(采用覆盖索引)
|
1
2
|
select LoginID,JobTitle,VacationHours,SickLeaveHours from EmployeeOp where VacationHours>60and SickLeaveHours>10--nc_employee_vacationsickleavehoursinclude--0.0048<br><br>select LoginID,JobTitle,VacationHours,SickLeaveHours from EmployeeOp where VacationHours>60<br>--nc_employee_vacationsickleavehoursinclude |
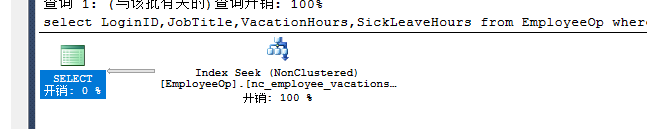
执行:(指定使用的索引)
|
1
2
3
|
select LoginID,JobTitle,VacationHours,SickLeaveHours from EmployeeOpwith(index=0) where VacationHours>60and SickLeaveHours>10 |
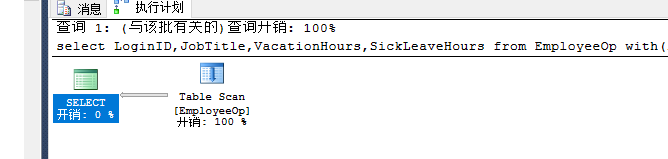
索引的优化:
|
1
|
select * from EmployeeOp<br>--创建非聚集索引<br>create nonclustered index nc_EmployeeOp on employeeop (VacationHours,SickLeaveHours) include (LoginID,JobTitle)<br><br>create nonclustered index nc_EmployeeOp_Vacation on employeeop(VacationHours)<br>include(LoginID,JobTitle)<br><br>--创建聚集索引<br>set statistics io on<br>create clustered index c_Employee_id on employeeop(BusinessEntityID) --7,9,9<br>set statistics io off |
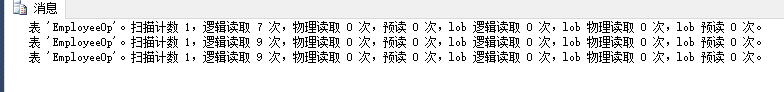
总结:先创建聚集索引在创非聚集索引
聚集索引键宽与窄:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
create table temptable(c1 int not null,c2 int) declare @c int set @c=0 while @c<50000 begin insert temptable values(@c,@c) set @c=@c+1 endcreate clustered index c_temptable_c1 on temptable(c1)set statistics io onselect * from temptable where c1<=25000 --0.07set statistics io off |
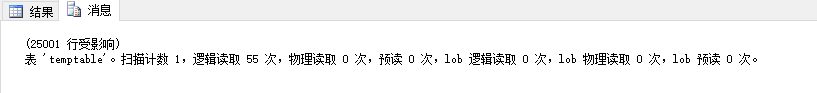
创建Guid的列:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
create table temptable(c1 uniqueidentifier,c2 int)declare @c int set @c=0 while @c<50000 begin insert temptable values(newid(),@c) set @c=@c+1 end create clustered index c_temptable_c1 on temptable(c1)set statistics io onselect * from temptable where c1<='D144242D-BFA3-4A8C-8DCE-C35A880E8BBE' --0.11set statistics io off |

索引设计建议:
1.where子句与连接条件列(where子句后面的列建立非聚集索引,有多列查询做成组合索引,并用inclued的方式把经常访问的列信息给包含到非聚集索引的页集,查询用到链接时(join):join的条件列做到非聚集索引中)
2.使用窄索引:索引列少、索引列数据类型空间少
1.减少IO数量
2.提高缓存效率
3.减少数据存储的空间
4.动态管理视图: sys.dm_db_index_physical_stats
选择性能高的列应该创建索引,如果有多列筛选,并尽量放置经常筛选的列和低密度的列到组合索引前面
int类型上创建索引与char 型上创建索引
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
create nonclustered index nc_employee_vacationsickleavehours on employeeop(vacationhours,sickleavehours) include(LoginID,JobTitle)create nonclustered index nc_employee_sickvacationleavehours on employeeop(sickleavehours,vacationhours)include(LoginID,JobTitle)select LoginID,JobTitle from EmployeeOp where VacationHours>40 and SickLeaveHours>90 -- nc_sickleavevacation |
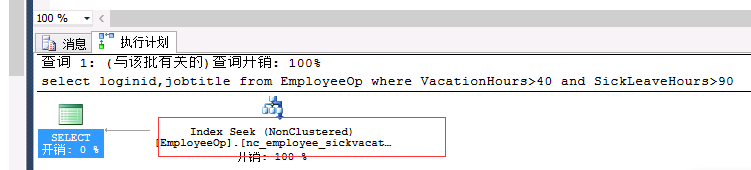
|
1
|
select loginid,jobtitle from EmployeeOp where VacationHours>99 and SickLeaveHours>10--nc_vacationsickleave |
总结:会自动进行筛选与and的顺序无关。(谁的选择性度高)
非聚集索引:RID指针指向堆得行标识符或聚集索引的键值
如果有非聚集索引,一定要创建一个聚集索引
先创建聚集索引,在创建非聚集索引
保持聚集索引窄:提高非聚集索引性能,提高聚集索引性能
使用聚集索引的时机:
1.Group by列
2.Order by 列
3.没有针对某个筛选条件的非聚集索引
不合适使用聚集索引:
1.索引列值频繁跟新:频繁跟新非聚集索引降低性能
2.并发的大量的插入
如果非聚集索引需要书签查找,则建议通过聚集索引查找
建议创建覆盖索引
不适合使用非聚集索引:
1.需要获取大量的行
2.需要获取大量的字段
交叉索引:针对筛选条件分别建立非聚集索引,在查询时,获得两个子集的索引交叉,解决覆盖索引非常宽的问题
建议使用过滤索引:针对查询必然需要筛选掉的条件做成索引的过滤条件
|
1
|
create nonclustered index nc_employee_sickvacationleavehours on employeeop(sickleavehours,vacationhours) include (LoginID,JobTitle) where salariedFlag=1 |
恰当使用索引视图使连接与聚合实物化,平衡查询性能提升与维护视图性能开销
复合索引每列可以不按照相同排序规则
可以在计算列上创建索引,建议使用持久化的计算列
指定并行度CPU个数、制定联机索引
经常使用数据库引擎优化顾问
尽量减少书签查找
查询优化统计方面的应用:
查询优化器对索引的选择依赖于统计
统计被自动创建和更新,也可以设置异步更新统计
通过Profiler跟踪统计事件
过时统计造成查询优化器无法选择最优的执行计划
自动创建统计也会在非索引列上创建统计
跟新自动统计:
SQL完成情况:

开启跟踪:
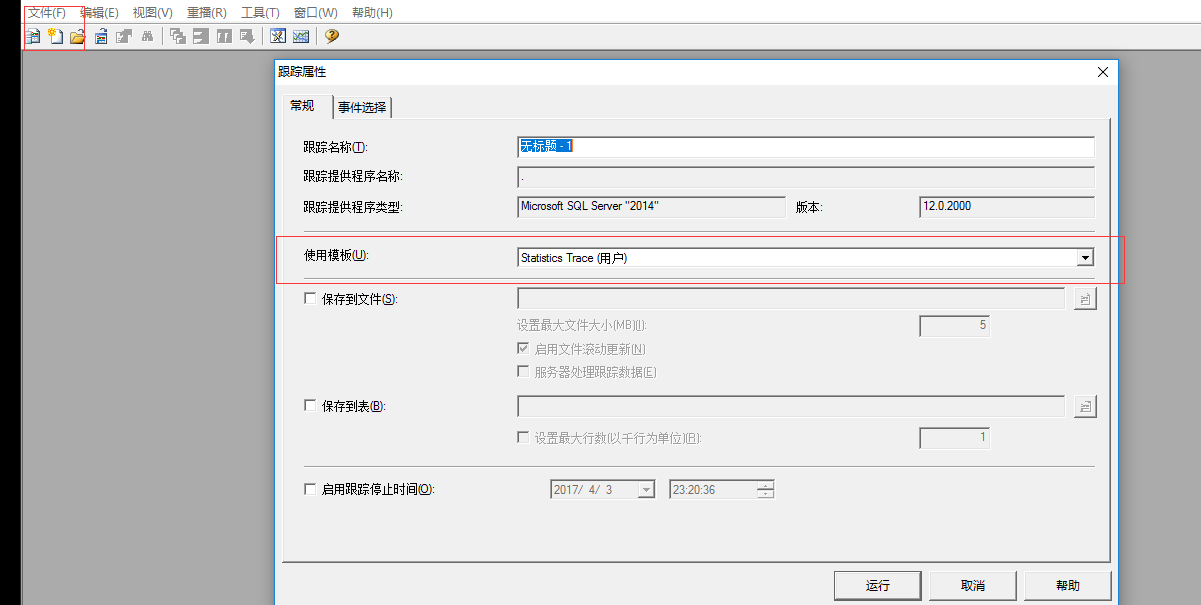
验证事件:
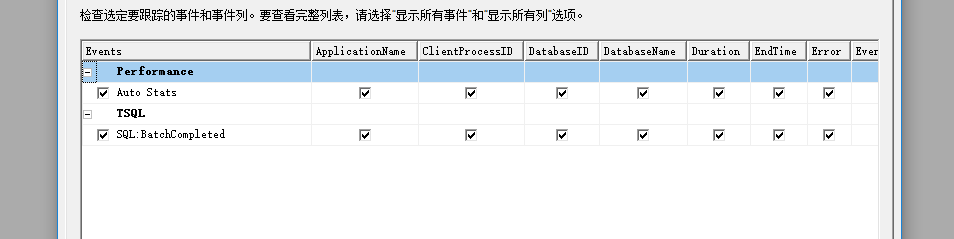
创建跟踪统计的表:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
create table StatisticsTB(c1 int identity(1,1),c2 int)declare @n intset @n=0while @n<5000begin insert StatisticsTB values(@n) set @n=@n+1endcreate nonclustered index nc_StatisticsTB_t2 on StatisticsTB(c2)declare @n intset @n=5001while @n<50000begininsert StatisticsTB values(@n)set @n=@n+1endselect * from StatisticsTB where c2<10--index select * from StatisticsTB where c2>10--Scan |
自动统计功能出现故障:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
--自动统计出现故障后declare @n intset @n=50001while @n<130000begininsert StatisticsTB values(@n)set @n=@n+1end |
本来是表扫描的就弄成索引。
|
1
|
select * from StatisticsTB where c2>4990--index |
查看统计信息:
|
1
2
3
4
|
--查看统计信息dbcc show_statistics('Employeeop',nc_Employee_vacation)--密度:0.01dbcc show_statistics('Employeeop',nc_Employee_vacationsickleave)--密度:0.009 |
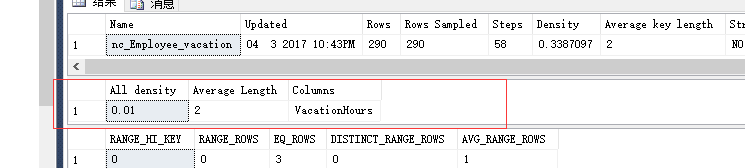
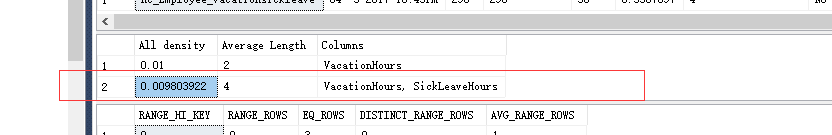
更新统计:
|
1
2
3
4
|
--更新统计 use HRDBgoSp_Updatestats |
–创建统计:
|
1
|
create statistics s_Employee_c2 on StatisticsTB(c2) |
在非索引列上创建统计:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
create table t1(c1 int identity(1,1),c2 int)insert t1 values(2)declare @count intset @count=0while @count<1000begininsert t1 values(1)set @count=@count+1endcreate table t2(c1 int identity(1,1),c2 int)insert t2 values(1)declare @count intset @count=0while @count<1000begininsert t1 values(2)set @count=@count+1end |
关闭统计的情况:
|
1
2
|
select t.c1,t.c2,tt.c1,tt.c2 from t1 as t inner join t2 as tt ont.c2=tt.c2--0.045 |
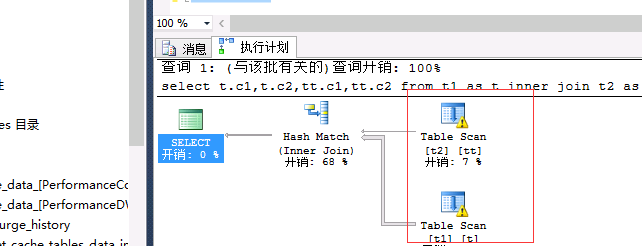
删除重新创建表:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
drop table t1drop table t2create table t1(c1 int identity(1,1),c2 int)insert t1 values(2)declare @count intset @count=0while @count<1000begininsert t1 values(1)set @count=@count+1endcreate table t2(c1 int identity(1,1),c2 int)insert t2 values(1)declare @count intset @count=0while @count<1000begininsert t1 values(2)set @count=@count+1endselect t.c1,t.c2,tt.c1,tt.c2 from t1 as t inner join t2 as tt ont.c2=tt.c2--0.045 |
统计建议:

查看索引是否有碎片:
|
1
2
3
|
--查看索引是否有碎片select * from sys.dm_db_index_physical_stats(db_id('HRDB'),object_id('EmployeeOp'),null,null,'Detailed') |
做碎片的整理:
|
1
|
--对页面进行重排:<br>alter index nc_Employee_Vacation on EmployeeOp Reorganize |
重建索引:
|
1
|
alter index nc_Employee_Vacation on employeeop rebuild with(fillfactor=40) |
填充因子的方式重建索引:
|
1
2
|
--指定填充因子重建索引create nonclustered index nc_Employee_Vacation on Employeeop (VacationHours) with(fillfactor=40,drop_existing=on) |
查询优化器Join的选择:
1.嵌套循环的join NestedLoop Join
2.合并的join Merge Join算法
1.链接表记录数都比较多,并且针对连接列进行了物理排序
2.Inner表的行有范围约束
3.Hash join算法
对Join算法的选择:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
create table parenttb(c1 int,name varchar(500))declare @c intset @c=0while @c<10begininsert parenttb values(@c,GETDATE())set @c=@c+1endgocreate table subtb(c1 int,cardid uniqueidentifier)declare @c intset @c=0while @c<250begininsert subtb values(@c,NEWID())set @c=@c+1end |
执行语句:
|
1
|
select p.name,s.cardid from parenttb as p inner join subtb as s on p.c1=s.c1 --hash --0.29 io: |
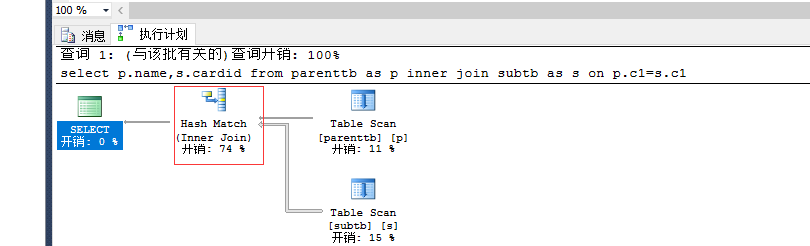
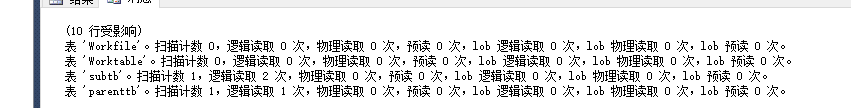
手工指定:
|
1
2
3
4
|
set statistics io onselect p.name,s.cardid from parenttb as p inner loop join subtb as s on p.c1=s.c1--nested loop --0.21 io:p 1 s 20set statistics io off |
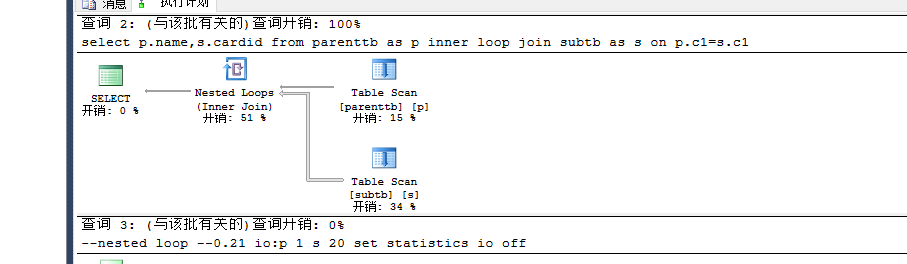
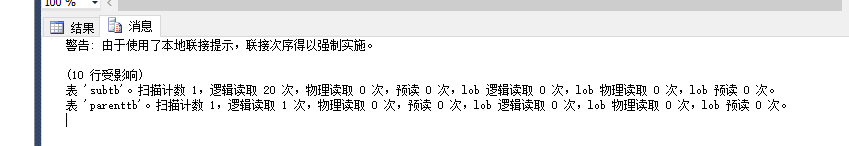
多添加一些记录:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
create table parenttb(c1 int,name varchar(500))declare @c intset @c=0while @c<1000begininsert parenttb values(@c,getdate())set @c=@c+1endgocreate table subtb(c1 int,cardid uniqueidentifier)declare @c intset @c=0while @c<25000begininsert subtb values(@c,NEWID())set @c=@c+1end |
执行语句:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
set statistics io onselect p.name,s.cardid from parenttb as p inner join subtb as s on p.c1=s.c1--hash --0.5 io:p 7 s 140set statistics io offset statistics io onselect p.name,s.cardid from parenttb as p inner loop join subtb as s on p.c1=s.c1--loop --64 io:p 7 s 560set statistics io off |
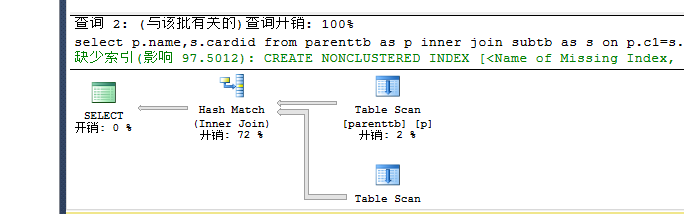

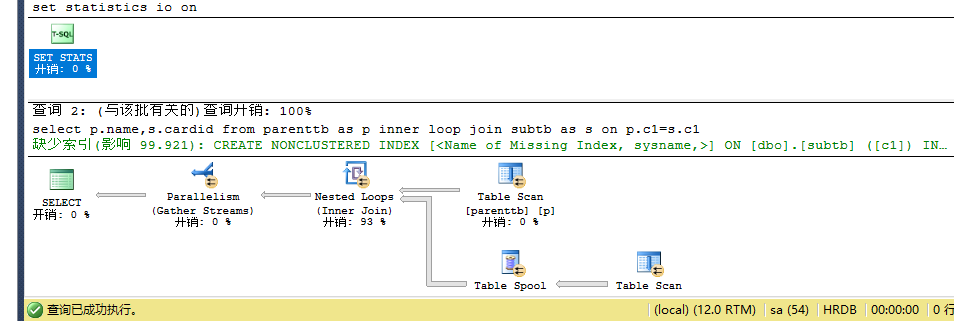

创建唯一的聚集索引:
|
1
2
3
|
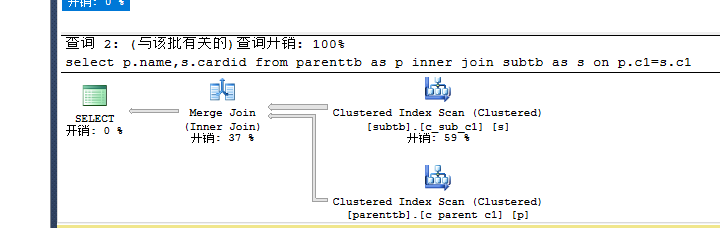
--创建唯一的聚集索引create unique clustered index c_parent_c1 on Parenttb(c1)create unique clustered index c_sub_c1 on Subtb(c1) |
执行:
|
1
2
3
|
set statistics io onselect p.name,s.cardid from parenttb as p inner join subtb as s on p.c1=s.c1--Merge --0.16 io:p 6 s 7set statistics io off |

 Mikel
Mikel

