服务(Service)对于大家来说一定不会陌生,它是Windows 操作系统重要的组成部分。我们可以把服务想像成一种特殊的应用程序,它随系统的“开启~关闭”而“开始~停止”其工作内容,在这期间无需任何用户参与。
Windows 服务在后台执行着各种各样任务,支持着我们日常的桌面操作。有时候可能需要服务与用户进行信息或界面交互操作,这种方式在XP 时代是没有问题的,但自从Vista 开始你会发现这种方式似乎已不起作用。
Session 0 隔离实验
下面来做一个名叫AlertService 的服务,它的作用就是向用户发出一个提示对话框,我们看看这个服务在Windows 7 中会发生什么情况。
using System.ServiceProcess;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace AlertService
{
public partial class Service1 : ServiceBase
{
public Service1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
protected override void OnStart(string[] args)
{
MessageBox.Show("A message from AlertService.");
}
protected override void OnStop()
{
}
}
}
程序编译后通过Installutil 将其加载到系统服务中:
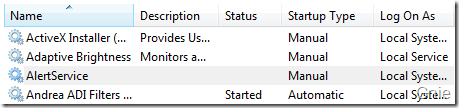
在服务属性中勾选“Allow service to interact with desktop” ,这样可以使AlertService 与桌面用户进行交互。
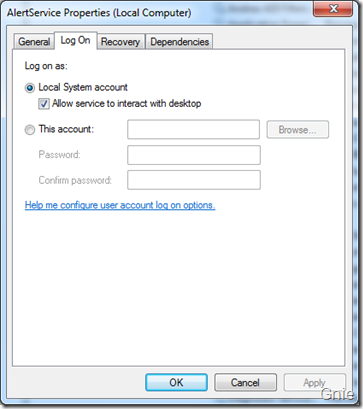
在服务管理器中将AlertService 服务“启动”,这时任务栏中会闪动一个图标:
![]()
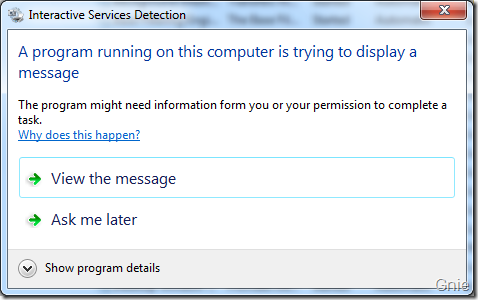
点击该图标会显示下面窗口,提示有个程序(AlertService)正在试图显示信息,是否需要浏览该信息:
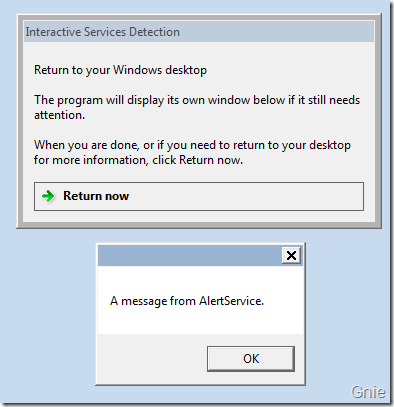
尝试点击“View the message”,便会显示下图界面(其实这个界面我已经不能从当前桌面操作截图了,是通过Virtual PC 截屏的,其原因请继续阅读)。注意观察可以发现下图的桌面背景已经不是Windows 7 默认的桌面背景了,说明AlertService 与桌面系统的Session 并不相同,这就是Session 0 隔离作用的结果。
Session 0 隔离原理
在Windows XP、Windows Server 2003 或早期Windows 系统时代,当第一个用户登录系统后服务和应用程序是在同一个Session 中运行的。这就是Session 0 如下图所示:
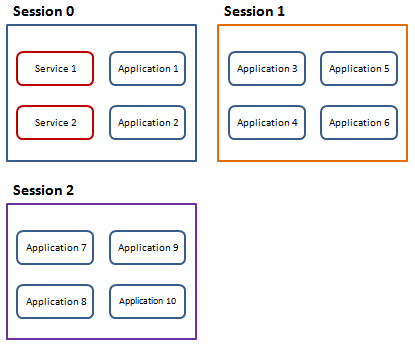
但是这种运行方式提高了系统安全风险,因为服务是通过提升了用户权限运行的,而应用程序往往是那些不具备管理员身份的普通用户运行的,其中的危险显而易见。
从Vista 开始Session 0 中只包含系统服务,其他应用程序则通过分离的Session 运行,将服务与应用程序隔离提高系统的安全性。如下图所示:
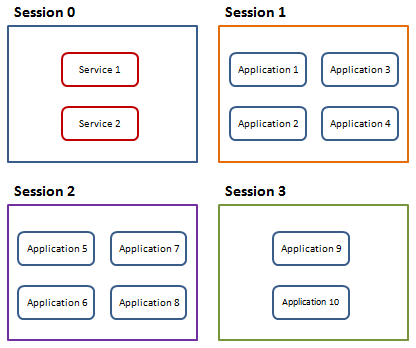
这样使得Session 0 与其他Session 之间无法进行交互,不能通过服务向桌面用户弹出信息窗口、UI 窗口等信息。这也就是为什么刚才我说那个图已经不能通过当前桌面进行截图了。

Session 检查
在实际开发过程中,可以通过Process Explorer 检查服务或程序处于哪个Session,会不会遇到Session 0 隔离问题。我们在Services 中找到之前加载的AlertService 服务,右键属性查看其Session 状态。
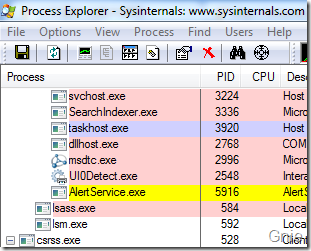
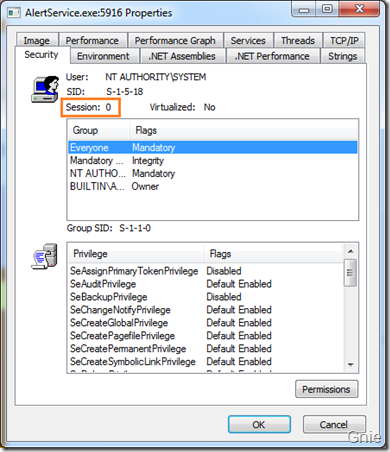
可看到AlertService 处于Session 0 中:
再来看看Outlook 应用程序:
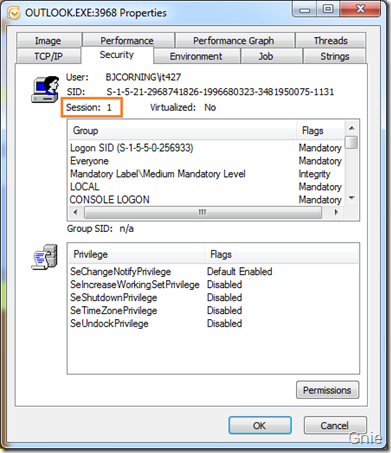
很明显在Windows 7 中服务和应用程序是处于不同的Session,它们之间加隔了一个保护墙,在下篇文章中将介绍如何穿过这堵保护墙使服务与桌面用户进行交互操作。
如果在开发过程中确实需要服务与桌面用户进行交互,可以通过远程桌面服务的API 绕过Session 0 的隔离完成交互操作。
对于简单的交互,服务可以通过WTSSendMessage 函数,在用户Session 上显示消息窗口。对于一些复杂的UI 交互,必须调用CreateProcessAsUser 或其他方法(WCF、.NET远程处理等)进行跨Session 通信,在桌面用户上创建一个应用程序界面。
WTSSendMessage 函数
如果服务只是简单的向桌面用户Session 发送消息窗口,则可以使用WTSSendMessage 函数实现。首先,在上一篇下载的代码中加入一个Interop.cs 类,并在类中加入如下代码:
public static IntPtr WTS_CURRENT_SERVER_HANDLE = IntPtr.Zero;
public static void ShowMessageBox(string message, string title)
{
int resp = 0;
WTSSendMessage(
WTS_CURRENT_SERVER_HANDLE,
WTSGetActiveConsoleSessionId(),
title, title.Length,
message, message.Length,
0, 0, out resp, false);
}
[DllImport("kernel32.dll", SetLastError = true)]
public static extern int WTSGetActiveConsoleSessionId();
[DllImport("wtsapi32.dll", SetLastError = true)]
public static extern bool WTSSendMessage(
IntPtr hServer,
int SessionId,
String pTitle,
int TitleLength,
String pMessage,
int MessageLength,
int Style,
int Timeout,
out int pResponse,
bool bWait);
在ShowMessageBox 函数中调用了WTSSendMessage 来发送信息窗口,这样我们就可以在Service 的OnStart 函数中使用,打开Service1.cs 加入下面代码:
protected override void OnStart(string[] args)
{
Interop.ShowMessageBox("This a message from AlertService.",
"AlertService Message");
}
编译程序后在服务管理器中重新启动AlertService 服务,从下图中可以看到消息窗口是在当前用户桌面显示的,而不是Session 0 中。
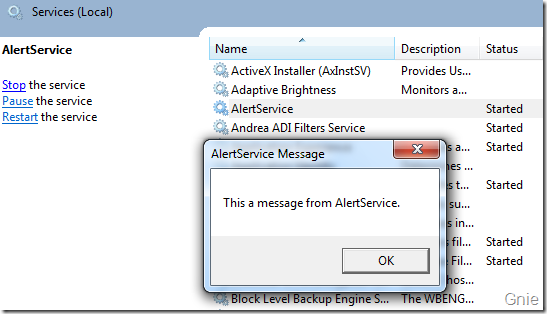
CreateProcessAsUser 函数
如果想通过服务向桌面用户Session 创建一个复杂UI 程序界面,则需要使用CreateProcessAsUser 函数为用户创建一个新进程用来运行相应的程序。打开Interop 类继续添加下面代码:
public static void CreateProcess(string app, string path)
{
bool result;
IntPtr hToken = WindowsIdentity.GetCurrent().Token;
IntPtr hDupedToken = IntPtr.Zero;
PROCESS_INFORMATION pi = new PROCESS_INFORMATION();
SECURITY_ATTRIBUTES sa = new SECURITY_ATTRIBUTES();
sa.Length = Marshal.SizeOf(sa);
STARTUPINFO si = new STARTUPINFO();
si.cb = Marshal.SizeOf(si);
int dwSessionID = WTSGetActiveConsoleSessionId();
result = WTSQueryUserToken(dwSessionID, out hToken);
if (!result)
{
ShowMessageBox("WTSQueryUserToken failed", "AlertService Message");
}
result = DuplicateTokenEx(
hToken,
GENERIC_ALL_ACCESS,
ref sa,
(int)SECURITY_IMPERSONATION_LEVEL.SecurityIdentification,
(int)TOKEN_TYPE.TokenPrimary,
ref hDupedToken
);
if (!result)
{
ShowMessageBox("DuplicateTokenEx failed" ,"AlertService Message");
}
IntPtr lpEnvironment = IntPtr.Zero;
result = CreateEnvironmentBlock(out lpEnvironment, hDupedToken, false);
if (!result)
{
ShowMessageBox("CreateEnvironmentBlock failed", "AlertService Message");
}
result = CreateProcessAsUser(
hDupedToken,
app,
String.Empty,
ref sa, ref sa,
false, 0, IntPtr.Zero,
path, ref si, ref pi);
if (!result)
{
int error = Marshal.GetLastWin32Error();
string message = String.Format("CreateProcessAsUser Error: {0}", error);
ShowMessageBox(message, "AlertService Message");
}
if (pi.hProcess != IntPtr.Zero)
CloseHandle(pi.hProcess);
if (pi.hThread != IntPtr.Zero)
CloseHandle(pi.hThread);
if (hDupedToken != IntPtr.Zero)
CloseHandle(hDupedToken);
}
[StructLayout(LayoutKind.Sequential)]
public struct STARTUPINFO
{
public Int32 cb;
public string lpReserved;
public string lpDesktop;
public string lpTitle;
public Int32 dwX;
public Int32 dwY;
public Int32 dwXSize;
public Int32 dwXCountChars;
public Int32 dwYCountChars;
public Int32 dwFillAttribute;
public Int32 dwFlags;
public Int16 wShowWindow;
public Int16 cbReserved2;
public IntPtr lpReserved2;
public IntPtr hStdInput;
public IntPtr hStdOutput;
public IntPtr hStdError;
}
[StructLayout(LayoutKind.Sequential)]
public struct PROCESS_INFORMATION
{
public IntPtr hProcess;
public IntPtr hThread;
public Int32 dwProcessID;
public Int32 dwThreadID;
}
[StructLayout(LayoutKind.Sequential)]
public struct SECURITY_ATTRIBUTES
{
public Int32 Length;
public IntPtr lpSecurityDescriptor;
public bool bInheritHandle;
}
public enum SECURITY_IMPERSONATION_LEVEL
{
SecurityAnonymous,
SecurityIdentification,
SecurityImpersonation,
SecurityDelegation
}
public enum TOKEN_TYPE
{
TokenPrimary = 1,
TokenImpersonation
}
public const int GENERIC_ALL_ACCESS = 0x10000000;
[DllImport("kernel32.dll", SetLastError = true,
CharSet = CharSet.Auto, CallingConvention = CallingConvention.StdCall)]
public static extern bool CloseHandle(IntPtr handle);
[DllImport("advapi32.dll", SetLastError = true,
CharSet = CharSet.Ansi, CallingConvention = CallingConvention.StdCall)]
public static extern bool CreateProcessAsUser(
IntPtr hToken,
string lpApplicationName,
string lpCommandLine,
ref SECURITY_ATTRIBUTES lpProcessAttributes,
ref SECURITY_ATTRIBUTES lpThreadAttributes,
bool bInheritHandle,
Int32 dwCreationFlags,
IntPtr lpEnvrionment,
string lpCurrentDirectory,
ref STARTUPINFO lpStartupInfo,
ref PROCESS_INFORMATION lpProcessInformation);
[DllImport("advapi32.dll", SetLastError = true)]
public static extern bool DuplicateTokenEx(
IntPtr hExistingToken,
Int32 dwDesiredAccess,
ref SECURITY_ATTRIBUTES lpThreadAttributes,
Int32 ImpersonationLevel,
Int32 dwTokenType,
ref IntPtr phNewToken);
[DllImport("wtsapi32.dll", SetLastError=true)]
public static extern bool WTSQueryUserToken(
Int32 sessionId,
out IntPtr Token);
[DllImport("userenv.dll", SetLastError = true)]
static extern bool CreateEnvironmentBlock(
out IntPtr lpEnvironment,
IntPtr hToken,
bool bInherit);
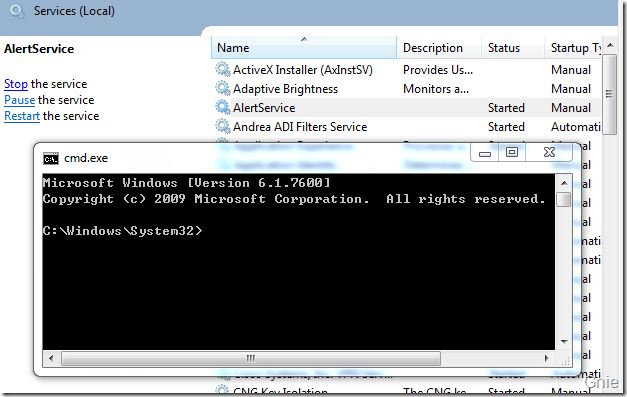
在CreateProcess 函数中同时也涉及到DuplicateTokenEx、WTSQueryUserToken、CreateEnvironmentBlock 函数的使用,有兴趣的朋友可通过MSDN 进行学习。完成CreateProcess 函数创建后,就可以真正的通过它来调用应用程序了,回到Service1.cs 修改一下OnStart 我们来打开一个CMD 窗口。如下代码:
protected override void OnStart(string[] args)
{
Interop.CreateProcess("cmd.exe",@"C:\Windows\System32\");
}
重新编译程序,启动AlertService 服务便可看到下图界面。至此,我们已经可以通过一些简单的方法对Session 0 隔离问题进行解决。大家也可以通过WCF 等技术完成一些更复杂的跨Session 通信方式,实现在Windows 7 及Vista 系统中服务与桌面用户的交互操作。
 Mikel
Mikel

