来源: YOLO-V4源码详解 – 爱旅行的球迷Engineer – 博客园
一. 整体架构
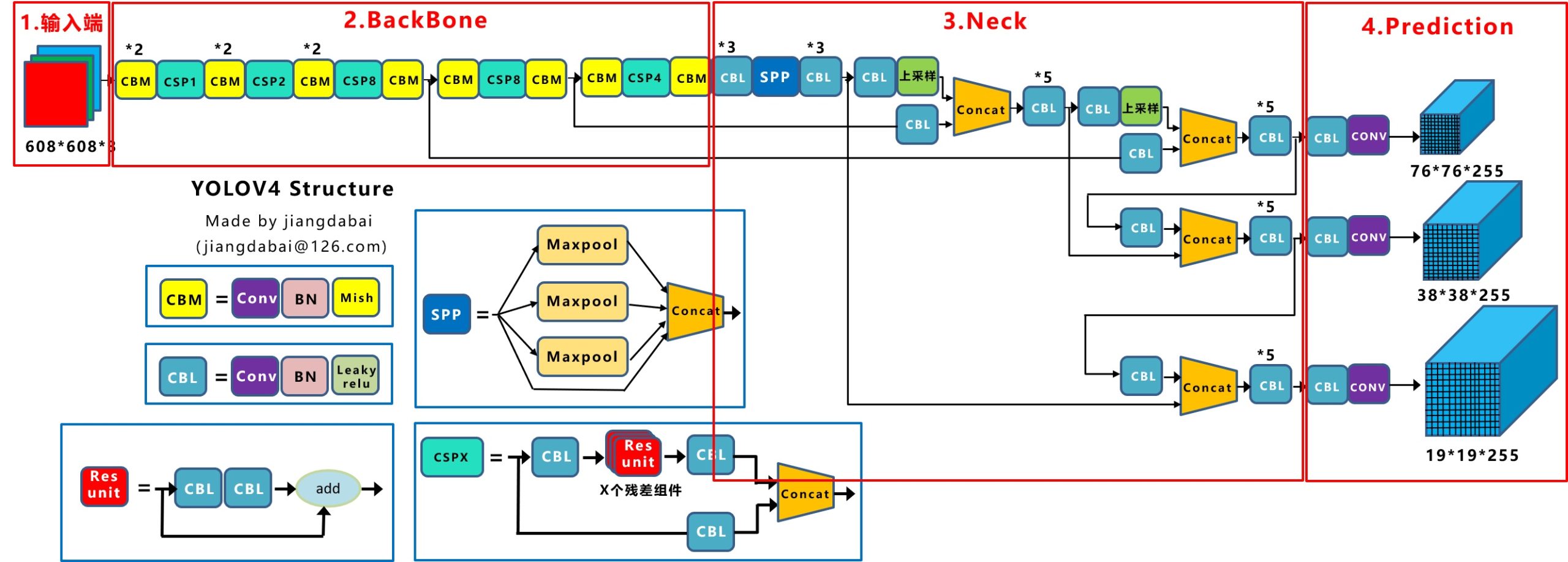
整体架构和YOLO-V3相同(感谢知乎大神@江大白),创新点如下:
输入端 –> Mosaic数据增强、cmBN、SAT自对抗训练;
BackBone –> CSPDarknet53、Mish激活函数、Dropblock;
Neck –> SPP、FPN+PAN结构;
Prediction –> GIOU_Loss、DIOU_nms。
二. 输入端
1. 数据加载流程(以训练为例)
“darknet/src/darknet.c”–main()函数:模型入口。
......
// 根据指令进入不同的函数。
if (0 == strcmp(argv[1], "average")){
average(argc, argv);
} else if (0 == strcmp(argv[1], "yolo")){
run_yolo(argc, argv);
} else if (0 == strcmp(argv[1], "voxel")){
run_voxel(argc, argv);
} else if (0 == strcmp(argv[1], "super")){
run_super(argc, argv);
} else if (0 == strcmp(argv[1], "detector")){
run_detector(argc, argv); // detector.c中,run_detector函数入口,detect操作,包括训练、测试等。
} else if (0 == strcmp(argv[1], "detect")){
float thresh = find_float_arg(argc, argv, "-thresh", .24);
int ext_output = find_arg(argc, argv, "-ext_output");
char *filename = (argc > 4) ? argv[4]: 0;
test_detector("cfg/coco.data", argv[2], argv[3], filename, thresh, 0.5, 0, ext_output, 0, NULL, 0, 0);
......
“darknet/src/detector.c”–run_detector()函数:train指令入口。
......
if (0 == strcmp(argv[2], "test")) test_detector(datacfg, cfg, weights, filename, thresh, hier_thresh, dont_show, ext_output, save_labels, outfile, letter_box, benchmark_layers); // 测试test_detector函数入口。
else if (0 == strcmp(argv[2], "train")) train_detector(datacfg, cfg, weights, gpus, ngpus, clear, dont_show, calc_map, mjpeg_port, show_imgs, benchmark_layers, chart_path); // 训练train_detector函数入口。
else if (0 == strcmp(argv[2], "valid")) validate_detector(datacfg, cfg, weights, outfile);
......
“darknet/src/detector.c”–train_detector()函数:数据加载入口。
pthread_t load_thread = load_data(args); // 首次创建并启动加载线程,args为模型训练参数。
“darknet/src/data.c”–load_data()函数:load_threads()分配线程。
pthread_t load_data(load_args args)
{
pthread_t thread;
struct load_args* ptr = (load_args*)xcalloc(1, sizeof(struct load_args));
*ptr = args;
/* 调用load_threads()函数。 */
if(pthread_create(&thread, 0, load_threads, ptr)) error("Thread creation failed"); // 参数1:指向线程标识符的指针;参数2:设置线程属性;参数3:线程运行函数的地址;参数4:运行函数的参数。
return thread;
}
“darknet/src/data.c”–load_threads()函数中:多线程调用run_thread_loop()。
if (!threads) {
threads = (pthread_t*)xcalloc(args.threads, sizeof(pthread_t));
run_load_data = (volatile int *)xcalloc(args.threads, sizeof(int));
args_swap = (load_args *)xcalloc(args.threads, sizeof(load_args));
fprintf(stderr, " Create %d permanent cpu-threads \n", args.threads);
for (i = 0; i < args.threads; ++i) {
int* ptr = (int*)xcalloc(1, sizeof(int));
*ptr = i;
if (pthread_create(&threads[i], 0, run_thread_loop, ptr)) error("Thread creation failed"); // 根据线程个数,调用run_thread_loop函数。
}
}
“darknet/src/data.c”–run_thread_loop函数:根据线程ID调用load_thread()。
void *run_thread_loop(void *ptr)
{
const int i = *(int *)ptr;
while (!custom_atomic_load_int(&flag_exit)) {
while (!custom_atomic_load_int(&run_load_data[i])) {
if (custom_atomic_load_int(&flag_exit)) {
free(ptr);
return 0;
}
this_thread_sleep_for(thread_wait_ms);
}
pthread_mutex_lock(&mtx_load_data);
load_args *args_local = (load_args *)xcalloc(1, sizeof(load_args));
*args_local = args_swap[i]; // 传入线程ID,在load_threads()函数中args_swap[i] = args。
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mtx_load_data);
load_thread(args_local); // 调用load_thread()函数。
custom_atomic_store_int(&run_load_data[i], 0);
}
free(ptr);
return 0;
}
“darknet/src/data.c”–load_thread()函数中:根据type标识符执行最底层的数据加载任务load_data_detection()。
else if (a.type == DETECTION_DATA){ // 用于检测的数据,在train_detector()函数中,args.type = DETECTION_DATA。
*a.d = load_data_detection(a.n, a.paths, a.m, a.w, a.h, a.c, a.num_boxes, a.classes, a.flip, a.gaussian_noise, a.blur, a.mixup, a.jitter, a.resize,
a.hue, a.saturation, a.exposure, a.mini_batch, a.track, a.augment_speed, a.letter_box, a.show_imgs);
“darknet/src/data.c”–load_data_detection()函数根据是否配置opencv,有两个版本,opencv版本中:
基本数据处理:
包括crop、flip、HSV augmentation、blur以及gaussian_noise。(注意,a.type == DETECTION_DATA时,无angle参数传入,没有图像旋转增强)
......
if (track) random_paths = get_sequential_paths(paths, n, m, mini_batch, augment_speed); // 目标跟踪。
else random_paths = get_random_paths(paths, n, m); // 随机选取n张图片的路径。
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
float *truth = (float*)xcalloc(5 * boxes, sizeof(float));
const char *filename = random_paths[i];
int flag = (c >= 3);
mat_cv *src;
src = load_image_mat_cv(filename, flag); // image_opencv.cpp中,load_image_mat_cv函数入口,使用opencv读取图像。
......
/* 将原图进行一定比例的缩放。 */
if (letter_box)
{
float img_ar = (float)ow / (float)oh; // 读取到的原始图像宽高比。
float net_ar = (float)w / (float)h; // 规定的,输入到网络要求的图像宽高比。
float result_ar = img_ar / net_ar; // 两者求比值来判断如何进行letter_box缩放。
if (result_ar > 1) // sheight - should be increased
{
float oh_tmp = ow / net_ar;
float delta_h = (oh_tmp - oh)/2;
ptop = ptop - delta_h;
pbot = pbot - delta_h;
}
else // swidth - should be increased
{
float ow_tmp = oh * net_ar;
float delta_w = (ow_tmp - ow)/2;
pleft = pleft - delta_w;
pright = pright - delta_w;
}
}
/* 执行letter_box变换。 */
int swidth = ow - pleft - pright;
int sheight = oh - ptop - pbot;
float sx = (float)swidth / ow;
float sy = (float)sheight / oh;
float dx = ((float)pleft / ow) / sx;
float dy = ((float)ptop / oh) / sy;
/* truth在调用函数后获得所有图像的标签信息,因为对原始图片进行了数据增强,其中的平移抖动势必会改动每个物体的矩形框标签信息,需要根据具体的数据增强方式进行相应矫正,后面的参数就是用于数据增强后的矩形框信息矫正。 */
int min_w_h = fill_truth_detection(filename, boxes, truth, classes, flip, dx, dy, 1. / sx, 1. / sy, w, h); // 求最小obj尺寸。
if ((min_w_h / 8) < blur && blur > 1) blur = min_w_h / 8; // disable blur if one of the objects is too small
// image_opencv.cpp中,image_data_augmentation函数入口,数据增强。
image ai = image_data_augmentation(src, w, h, pleft, ptop, swidth, sheight, flip, dhue, dsat, dexp, gaussian_noise, blur, boxes, truth);
......
“darknet/src/image_opencv.cpp”–image_data_augmentation()函数:
extern "C" image image_data_augmentation(mat_cv* mat, int w, int h, int pleft, int ptop, int swidth, int sheight, int flip,
float dhue, float dsat, float dexp, int gaussian_noise, int blur, int num_boxes, float *truth)
{
image out;
try {
cv::Mat img = *(cv::Mat *)mat; // 读取图像数据。
// crop
cv::Rect src_rect(pleft, ptop, swidth, sheight);
cv::Rect img_rect(cv::Point2i(0, 0), img.size());
cv::Rect new_src_rect = src_rect & img_rect;
cv::Rect dst_rect(cv::Point2i(std::max<int>(0, -pleft), std::max<int>(0, -ptop)), new_src_rect.size());
cv::Mat sized;
if (src_rect.x == 0 && src_rect.y == 0 && src_rect.size() == img.size()) {
cv::resize(img, sized, cv::Size(w, h), 0, 0, cv::INTER_LINEAR);
}
else {
cv::Mat cropped(src_rect.size(), img.type());
cropped.setTo(cv::mean(img));
img(new_src_rect).copyTo(cropped(dst_rect));
// resize
cv::resize(cropped, sized, cv::Size(w, h), 0, 0, cv::INTER_LINEAR);
}
// flip,虽然配置文件里没有flip参数,但代码里有使用。
if (flip) {
cv::Mat cropped;
cv::flip(sized, cropped, 1); // 0 - x-axis, 1 - y-axis, -1 - both axes (x & y)
sized = cropped.clone();
}
// HSV augmentation
if (dsat != 1 || dexp != 1 || dhue != 0) {
if (img.channels() >= 3)
{
cv::Mat hsv_src;
cvtColor(sized, hsv_src, cv::COLOR_RGB2HSV); // RGB to HSV
std::vector<cv::Mat> hsv;
cv::split(hsv_src, hsv);
hsv[1] *= dsat;
hsv[2] *= dexp;
hsv[0] += 179 * dhue;
cv::merge(hsv, hsv_src);
cvtColor(hsv_src, sized, cv::COLOR_HSV2RGB); // HSV to RGB (the same as previous)
}
else
{
sized *= dexp;
}
}
if (blur) {
cv::Mat dst(sized.size(), sized.type());
if (blur == 1) {
cv::GaussianBlur(sized, dst, cv::Size(17, 17), 0);
}
else {
int ksize = (blur / 2) * 2 + 1;
cv::Size kernel_size = cv::Size(ksize, ksize);
cv::GaussianBlur(sized, dst, kernel_size, 0);
}
if (blur == 1) {
cv::Rect img_rect(0, 0, sized.cols, sized.rows);
int t;
for (t = 0; t < num_boxes; ++t) {
box b = float_to_box_stride(truth + t*(4 + 1), 1);
if (!b.x) break;
int left = (b.x - b.w / 2.)*sized.cols;
int width = b.w*sized.cols;
int top = (b.y - b.h / 2.)*sized.rows;
int height = b.h*sized.rows;
cv::Rect roi(left, top, width, height);
roi = roi & img_rect;
sized(roi).copyTo(dst(roi));
}
}
dst.copyTo(sized);
}
if (gaussian_noise) {
cv::Mat noise = cv::Mat(sized.size(), sized.type());
gaussian_noise = std::min(gaussian_noise, 127);
gaussian_noise = std::max(gaussian_noise, 0);
cv::randn(noise, 0, gaussian_noise); //mean and variance
cv::Mat sized_norm = sized + noise;
sized = sized_norm;
}
// Mat -> image
out = mat_to_image(sized);
}
catch (...) {
cerr << "OpenCV can't augment image: " << w << " x " << h << " \n";
out = mat_to_image(*(cv::Mat*)mat);
}
return out;
}
高级数据处理:
主要是mosaic数据增强。
......
if (use_mixup == 0) { // 不使用mixup。
d.X.vals[i] = ai.data;
memcpy(d.y.vals[i], truth, 5 * boxes * sizeof(float)); // C库函数,从存储区truth复制5 * boxes * sizeof(float)个字节到存储区d.y.vals[i]。
}
else if (use_mixup == 1) { // 使用mixup。
if (i_mixup == 0) { // 第一个序列。
d.X.vals[i] = ai.data;
memcpy(d.y.vals[i], truth, 5 * boxes * sizeof(float)); // n张图的label->d.y.vals,i_mixup=1时,作为上一个sequence的label。
}
else if (i_mixup == 1) { // 第二个序列,此时d.X.vals已经储存上个序列n张增强后的图。
image old_img = make_empty_image(w, h, c);
old_img.data = d.X.vals[i]; // 记录上一个序列的n张old_img。
blend_images_cv(ai, 0.5, old_img, 0.5); // image_opencv.cpp中,blend_images_cv函数入口,新旧序列对应的两张图进行线性融合,ai只是在i_mixup和i循环最里层的一张图。
blend_truth(d.y.vals[i], boxes, truth); // 上一个序列的d.y.vals[i]与这个序列的truth融合。
free_image(old_img); // 释放img数据。
d.X.vals[i] = ai.data; // 保存这个序列的n张图。
}
}
else if (use_mixup == 3) { // mosaic数据增强。
if (i_mixup == 0) { // 第一序列,初始化。
image tmp_img = make_image(w, h, c);
d.X.vals[i] = tmp_img.data;
}
if (flip) { // 翻转。
int tmp = pleft;
pleft = pright;
pright = tmp;
}
const int left_shift = min_val_cmp(cut_x[i], max_val_cmp(0, (-pleft*w / ow))); // utils.h中,min_val_cmp函数入口,取小(min)取大(max)。
const int top_shift = min_val_cmp(cut_y[i], max_val_cmp(0, (-ptop*h / oh))); // ptop<0时,取cut_y[i]与-ptop*h / oh较小的,否则返回0。
const int right_shift = min_val_cmp((w - cut_x[i]), max_val_cmp(0, (-pright*w / ow)));
const int bot_shift = min_val_cmp(h - cut_y[i], max_val_cmp(0, (-pbot*h / oh)));
int k, x, y;
for (k = 0; k < c; ++k) { // 通道。
for (y = 0; y < h; ++y) { // 高度。
int j = y*w + k*w*h; // 每张图i,按行堆叠索引j。
if (i_mixup == 0 && y < cut_y[i]) { // 右下角区块,i_mixup=0~3,d.X.vals[i]未被清0,累计粘贴4块区域。
int j_src = (w - cut_x[i] - right_shift) + (y + h - cut_y[i] - bot_shift)*w + k*w*h;
memcpy(&d.X.vals[i][j + 0], &ai.data[j_src], cut_x[i] * sizeof(float)); // 由ai.data[j_src]所指内存区域复制cut_x[i]*sizeof(float)个字节到&d.X.vals[i][j + 0]所指内存区域。
}
if (i_mixup == 1 && y < cut_y[i]) { // 左下角区块。
int j_src = left_shift + (y + h - cut_y[i] - bot_shift)*w + k*w*h;
memcpy(&d.X.vals[i][j + cut_x[i]], &ai.data[j_src], (w-cut_x[i]) * sizeof(float));
}
if (i_mixup == 2 && y >= cut_y[i]) { // 右上角区块。
int j_src = (w - cut_x[i] - right_shift) + (top_shift + y - cut_y[i])*w + k*w*h;
memcpy(&d.X.vals[i][j + 0], &ai.data[j_src], cut_x[i] * sizeof(float));
}
if (i_mixup == 3 && y >= cut_y[i]) { // 左上角区块。
int j_src = left_shift + (top_shift + y - cut_y[i])*w + k*w*h;
memcpy(&d.X.vals[i][j + cut_x[i]], &ai.data[j_src], (w - cut_x[i]) * sizeof(float));
}
}
}
blend_truth_mosaic(d.y.vals[i], boxes, truth, w, h, cut_x[i], cut_y[i], i_mixup, left_shift, right_shift, top_shift, bot_shift); // label对应shift调整。
free_image(ai);
ai.data = d.X.vals[i];
}
......
三. BackBone
总图:
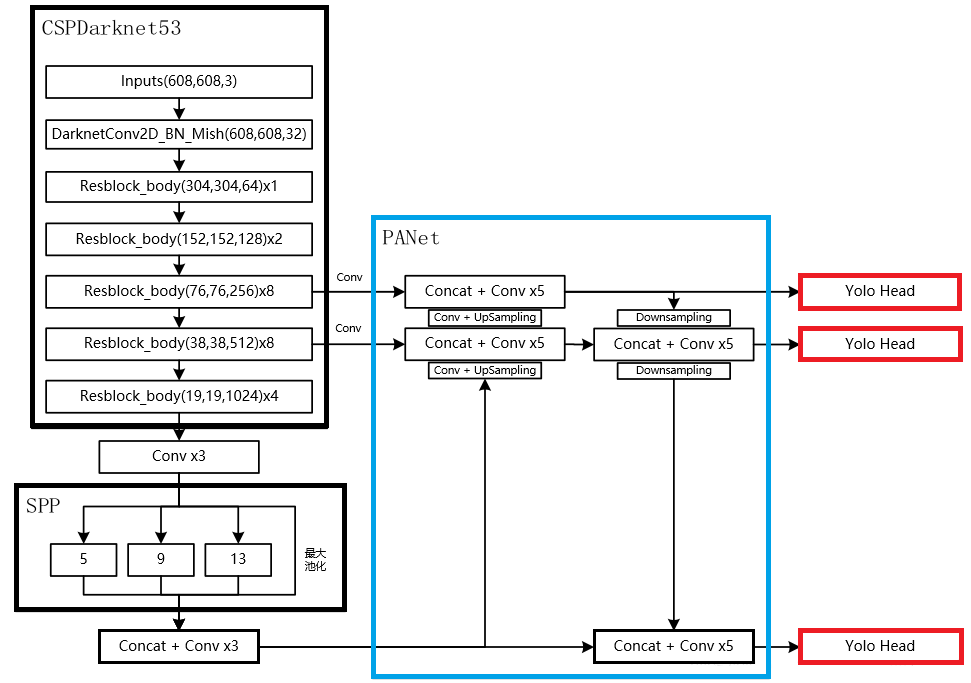
网络配置文件(.cfg)决定了模型架构,训练时需要在命令行指定。文件以[net]段开头,定义与训练直接相关的参数:
[net]
# Testing # 测试时,batch和subdivisions设置为1,否则可能出错。
#batch=1 # 大一些可以减小训练震荡及训练时NAN的出现。
#subdivisions=1 # 必须为为8的倍数,显存吃紧可以设成32或64。
# Training
batch=64 # 训练过程中将64张图一次性加载进内存,前向传播后将64张图的loss累加求平均,再一次性后向传播更新权重。
subdivisions=16 # 一个batch分16次完成前向传播,即每次计算4张。
width=608 # 网络输入的宽。
height=608 # 网络输入的高。
channels=3 # 网络输入的通道数。
momentum=0.949 # 动量梯度下降优化方法中的动量参数,更新的时候在一定程度上保留之前更新的方向。
decay=0.0005 # 权重衰减正则项,用于防止过拟合。
angle=0 # 数据增强参数,通过旋转角度来生成更多训练样本。
saturation = 1.5 # 数据增强参数,通过调整饱和度来生成更多训练样本。
exposure = 1.5 # 数据增强参数,通过调整曝光量来生成更多训练样本。
hue=.1 # 数据增强参数,通过调整色调来生成更多训练样本。
learning_rate=0.001 # 学习率。
burn_in=1000 # 在迭代次数小于burn_in时,学习率的更新为一种方式,大于burn_in时,采用policy的更新方式。
max_batches = 500500 #训练迭代次数,跑完一个batch为一次,一般为类别数*2000,训练样本少或train from scratch可适当增加。
policy=steps # 学习率调整的策略。
steps=400000,450000 # 动态调整学习率,steps可以取max_batches的0.8~0.9。
scales=.1,.1 # 迭代到steps(1)次时,学习率衰减十倍,steps(2)次时,学习率又会在前一个学习率的基础上衰减十倍。
#cutmix=1 # cutmix数据增强,将一部分区域cut掉但不填充0像素而是随机填充训练集中的其他数据的区域像素值,分类结果按一定的比例分配。
mosaic=1 # 马赛克数据增强,取四张图,随机缩放、随机裁剪、随机排布的方式拼接,详见上述代码分析。
其余区段,包括[convolutional]、[route]、[shortcut]、[maxpool]、[upsample]、[yolo]层,为不同类型的层的配置参数。YOLO-V4中[net]层之后堆叠多个CBM及CSP层,首先是2个CBM层,CBM结构如下:
[convolutional] batch_normalize=1 # 是否进行BN。 filters=32 # 卷积核个数,也就是该层的输出通道数。 size=3 # 卷积核大小。 stride=1 # 卷积步长。 pad=1 # pad边缘补像素。 activation=mish # 网络层激活函数,yolo-v4只在Backbone中采用了mish,网络后面仍采用Leaky_relu。
创新点是Mish激活函数,与Leaky_Relu曲线对比如图:
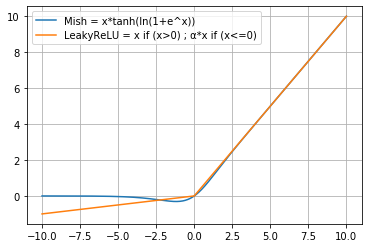
Mish在负值的时候并不是完全截断,而是允许比较小的负梯度流入,保证了信息的流动。此外,平滑的激活函数允许更好的信息深入神经网络,梯度下降效果更好,从而提升准确性和泛化能力。
两个CBM后是CSP1,CSP1结构如下:
# CSP1 = CBM + 1个残差unit + CBM -> Concat(with CBM),见总图。 [convolutional] # CBM层,直接与7层后的route层连接,形成总图中CSPX下方支路。 batch_normalize=1 filters=64 size=1 stride=1 pad=1 activation=mish [route] # 得到前面第2层的输出,即CSP开始位置,构建如图所示的CSP第一支路。 layers = -2 [convolutional] # CBM层。 batch_normalize=1 filters=64 size=1 stride=1 pad=1 activation=mish # Residual Block [convolutional] # CBM层。 batch_normalize=1 filters=32 size=1 stride=1 pad=1 activation=mish [convolutional] # CBM层。 batch_normalize=1 filters=64 size=3 stride=1 pad=1 activation=mish [shortcut] # add前面第3层的输出,Residual Block结束。 from=-3 activation=linear [convolutional] # CBM层。 batch_normalize=1 filters=64 size=1 stride=1 pad=1 activation=mish [route] # Concat上一个CBM层与前面第7层(CBM)的输出。 layers = -1,-7
接下来的CBM及CSPX架构与上述block相同,只是CSPX对应X个残差单元,如图:
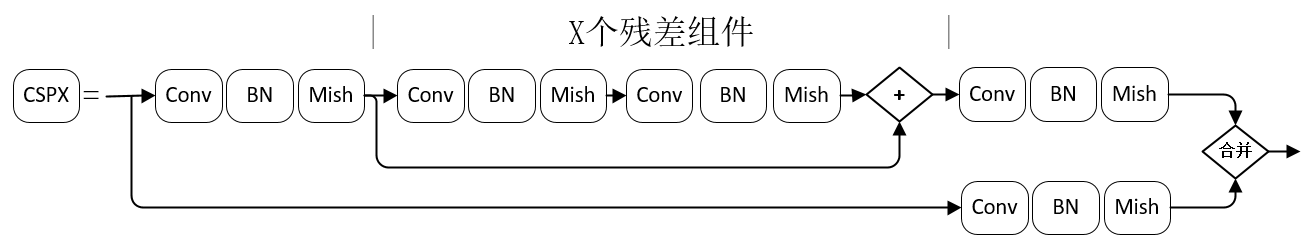
CSP模块将基础层的特征映射划分为两部分,再skip connection,减少计算量的同时保证了准确率。
要注意的是,backbone中两次出现分支,与后续Neck连接,稍后会解释。
四. Neck&Prediction
.cfg配置文件后半部分是Neck和YOLO-Prediction设置,我做了重点注释:
### CBL*3 ### [convolutional] batch_normalize=1 filters=512 size=1 stride=1 pad=1 activation=leaky # 不再使用Mish。 [convolutional] batch_normalize=1 size=3 stride=1 pad=1 filters=1024 activation=leaky [convolutional] batch_normalize=1 filters=512 size=1 stride=1 pad=1 activation=leaky ### SPP-最大池化的方式进行多尺度融合 ### [maxpool] # 5*5。 stride=1 size=5 [route] layers=-2 [maxpool] # 9*9。 stride=1 size=9 [route] layers=-4 [maxpool] # 13*13。 stride=1 size=13 [route] # Concat。 layers=-1,-3,-5,-6 ### End SPP ### ### CBL*3 ### [convolutional] batch_normalize=1 filters=512 size=1 stride=1 pad=1 activation=leaky # 不再使用Mish。 [convolutional] batch_normalize=1 size=3 stride=1 pad=1 filters=1024 activation=leaky [convolutional] batch_normalize=1 filters=512 size=1 stride=1 pad=1 activation=leaky ### CBL ### [convolutional] batch_normalize=1 filters=256 size=1 stride=1 pad=1 activation=leaky ### 上采样 ### [upsample] stride=2 [route] layers = 85 # 获取Backbone中CBM+CSP8+CBM模块的输出,85从net以外的层开始计数,从0开始索引。 [convolutional] # 增加CBL支路。 batch_normalize=1 filters=256 size=1 stride=1 pad=1 activation=leaky [route] # Concat。 layers = -1, -3 ### CBL*5 ### [convolutional] batch_normalize=1 filters=256 size=1 stride=1 pad=1 activation=leaky [convolutional] batch_normalize=1 size=3 stride=1 pad=1 filters=512 activation=leaky [convolutional] batch_normalize=1 filters=256 size=1 stride=1 pad=1 activation=leaky [convolutional] batch_normalize=1 size=3 stride=1 pad=1 filters=512 activation=leaky [convolutional] batch_normalize=1 filters=256 size=1 stride=1 pad=1 activation=leaky ### CBL ### [convolutional] batch_normalize=1 filters=128 size=1 stride=1 pad=1 activation=leaky ### 上采样 ### [upsample] stride=2 [route] layers = 54 # 获取Backbone中CBM*2+CSP1+CBM*2+CSP2+CBM*2+CSP8+CBM模块的输出,54从net以外的层开始计数,从0开始索引。 ### CBL ### [convolutional] batch_normalize=1 filters=128 size=1 stride=1 pad=1 activation=leaky [route] # Concat。 layers = -1, -3 ### CBL*5 ### [convolutional] batch_normalize=1 filters=128 size=1 stride=1 pad=1 activation=leaky [convolutional] batch_normalize=1 size=3 stride=1 pad=1 filters=256 activation=leaky [convolutional] batch_normalize=1 filters=128 size=1 stride=1 pad=1 activation=leaky [convolutional] batch_normalize=1 size=3 stride=1 pad=1 filters=256 activation=leaky [convolutional] batch_normalize=1 filters=128 size=1 stride=1 pad=1 activation=leaky ### Prediction ### ### CBL ### [convolutional] batch_normalize=1 size=3 stride=1 pad=1 filters=256 activation=leaky ### conv ### [convolutional] size=1 stride=1 pad=1 filters=255 activation=linear
mask = 0,1,2 # 当前属于第几个预选框。
# coco数据集默认值,可通过detector calc_anchors,利用k-means计算样本anchors,但要根据每个anchor的大小(是否超过60*60或30*30)更改mask对应的索引(第一个yolo层对应小尺寸;第二个对应中等大小;第三个对应大尺寸)及上一个conv层的filters。
anchors = 12, 16, 19, 36, 40, 28, 36, 75, 76, 55, 72, 146, 142, 110, 192, 243, 459, 401
classes=80 # 网络需要识别的物体种类数。
num=9 # 预选框的个数,即anchors总数。
jitter=.3 # 通过抖动增加噪声来抑制过拟合。
ignore_thresh = .7
truth_thresh = 1
scale_x_y = 1.2
iou_thresh=0.213
cls_normalizer=1.0
iou_normalizer=0.07
iou_loss=ciou # CIOU损失函数,考虑目标框回归函数的重叠面积、中心点距离及长宽比。
nms_kind=greedynms
beta_nms=0.6
max_delta=5
### CBL ###
[convolutional]
batch_normalize=1
size=3
stride=2
pad=1
filters=256
activation=leaky
layers = -1, -16
[convolutional]
batch_normalize=1
filters=256
size=1
stride=1
pad=1
activation=leaky
batch_normalize=1
size=3
stride=1
pad=1
filters=512
activation=leaky
batch_normalize=1
filters=256
size=1
stride=1
pad=1
activation=leaky
batch_normalize=1
size=3
stride=1
pad=1
filters=512
activation=leaky
batch_normalize=1
filters=256
size=1
stride=1
pad=1
activation=leaky
[convolutional]
batch_normalize=1
size=3
stride=1
pad=1
filters=512
activation=leaky
[convolutional]
size=1
stride=1
pad=1
filters=255
activation=linear
mask = 3,4,5
anchors = 12, 16, 19, 36, 40, 28, 36, 75, 76, 55, 72, 146, 142, 110, 192, 243, 459, 401
classes=80
num=9
jitter=.3
ignore_thresh = .7
truth_thresh = 1
scale_x_y = 1.1
iou_thresh=0.213
cls_normalizer=1.0
iou_normalizer=0.07
iou_loss=ciou
nms_kind=greedynms
beta_nms=0.6
max_delta=5
layers = -4
### CBL ###
[convolutional]
batch_normalize=1
size=3
stride=2
pad=1
filters=512
activation=leaky
layers = -1, -37
[convolutional]
batch_normalize=1
filters=512
size=1
stride=1
pad=1
activation=leaky
batch_normalize=1
size=3
stride=1
pad=1
filters=1024
activation=leaky
batch_normalize=1
filters=512
size=1
stride=1
pad=1
activation=leaky
batch_normalize=1
size=3
stride=1
pad=1
filters=1024
activation=leaky
batch_normalize=1
filters=512
size=1
stride=1
pad=1
activation=leaky
[convolutional]
batch_normalize=1
size=3
stride=1
pad=1
filters=1024
activation=leaky
[convolutional]
size=1
stride=1
pad=1
filters=255
activation=linear
mask = 6,7,8
anchors = 12, 16, 19, 36, 40, 28, 36, 75, 76, 55, 72, 146, 142, 110, 192, 243, 459, 401
classes=80
num=9
jitter=.3
ignore_thresh = .7
truth_thresh = 1
random=1
scale_x_y = 1.05
iou_thresh=0.213
cls_normalizer=1.0
iou_normalizer=0.07
iou_loss=ciou
nms_kind=greedynms
beta_nms=0.6
max_delta=5
其中第一个创新点是引入Spatial Pyramid Pooling(SPP)模块:
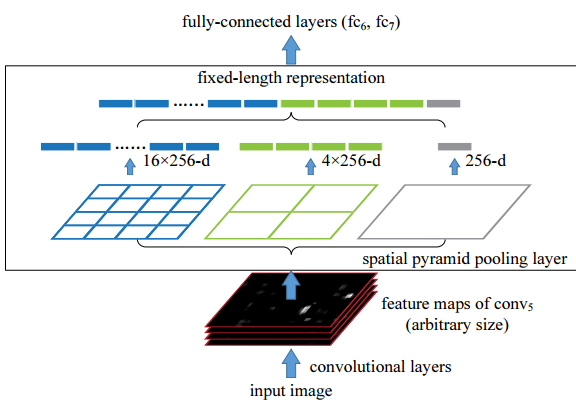
代码中max pool和route层组合,三个不同尺度的max-pooling将前一个卷积层输出的feature maps进行多尺度的特征处理,再与原图进行拼接,一共4个scale。相比于只用一个max-pooling,提取的特征范围更大,而且将不同尺度的特征进行了有效分离;
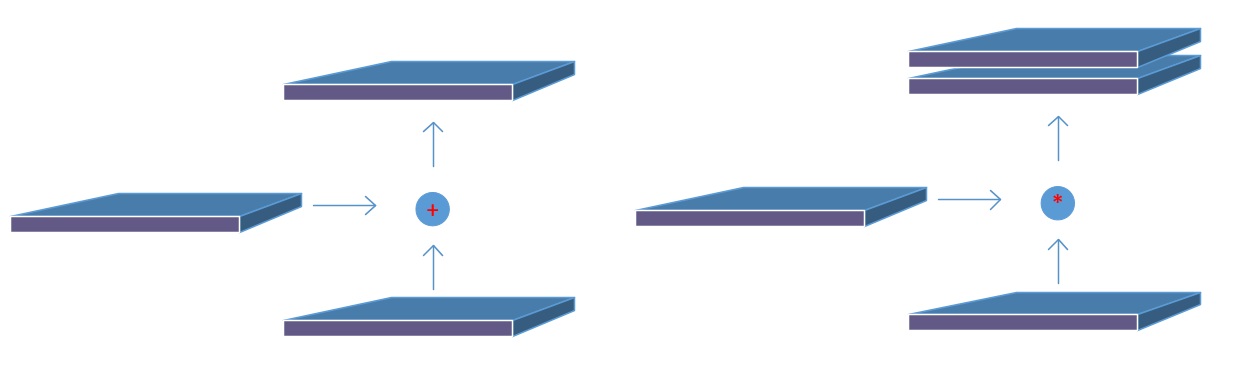
第二个创新点是在FPN的基础上引入PAN结构:
原版PANet中PAN操作是做element-wise相加,YOLO-V4则采用扩增维度的Concat,如下图:
 Backbone下采样不同阶段得到的特征图Concat后续上采样阶对应尺度的的output,形成FPN结构,再经过两个botton-up的PAN结构。
Backbone下采样不同阶段得到的特征图Concat后续上采样阶对应尺度的的output,形成FPN结构,再经过两个botton-up的PAN结构。
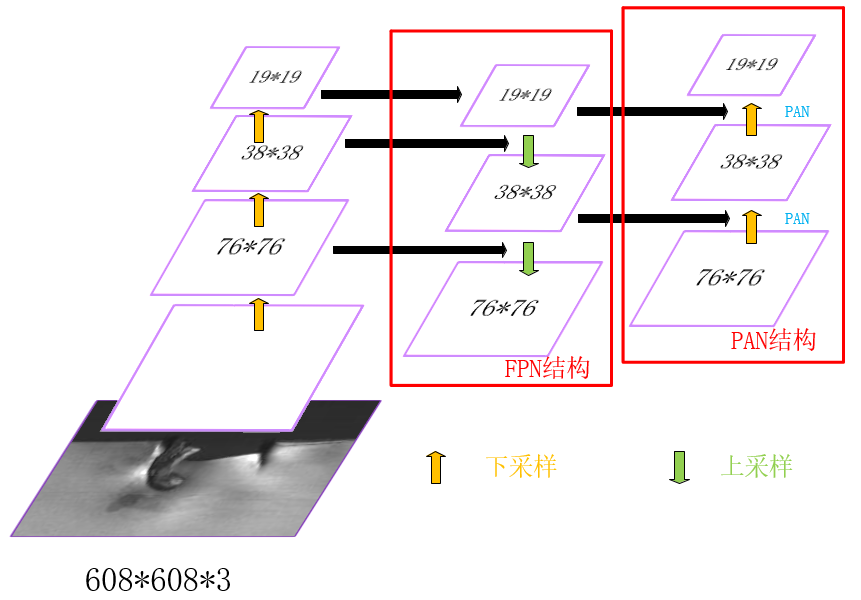
下采样1:前10个block中,只有3个CBM的stride为2,输入图像尺寸变为608/2*2*2=76,filters根据最后一个CBM为256,因此第10个block输出feature map为76*76*256;
下采样2:继续Backbone,同理,第13个block(CBM)输出38*38*512的特征图;
下采样3:第23个block(CBL)输出为19*19*512;
上采样1:下采样3 + CBL + 上采样 = 38*38*256;
Concat1:[上采样1] Concat [下采样2 + CBL] = [38*38*256] Concat [38*38*512 + (256,1)] = 38*38*512;
上采样2:Concat1 + CBL*5 + CBL + 上采样 = 76*76*128;
Concat2:[上采样2] Concat [下采样1 + CBL] = [76*76*128] Concat [76*76*256 + (128,1)] = 76*76*256;
Concat3(PAN1):[Concat2 + CBL*5 + CBL] Concat [Concat1 + CBL*5] = [76*76*256 + (128,1) + (256,2)] Concat [38*38*512 + (256,1)] = [38*38*256] Concat [38*38*256] = 38*38*512;
Concat4(PAN2):[Concat3 + CBL*5 + CBL] Concat [下采样3] = [38*38*512 + (256,1) + (512,2)] Concat [19*19*512] = 19*19*1024;
Prediction①:Concat2 + CBL*5 + CBL + conv = 76*76*256 + (128,1) + (256,1) + (filters,1) = 76*76*filters,其中filters = (class_num + 5)*3,图中默认COCO数据集,80类所以是255;
Prediction②:PAN1 + CBL*5 + CBL + conv = 38*38*512 + (256,1) + (512,1) + (filters,1) = 38*38*filters,其中filters = (class_num + 5)*3,图中默认COCO数据集,80类所以是255;
Prediction③:PAN2 + CBL*5 + CBL + conv = 19*19*1024 + (512,1) + (1024,1) + (filters,1) = 19*19*filters,其中filters = (class_num + 5)*3,图中默认COCO数据集,80类所以是255。
五. 网络构建
上述从backbone到prediction的网络架构,源码中都是基于network结构体来储存网络参数。具体流程如下:
“darknet/src/detector.c”–train_detector()函数中:
......
network net_map;
if (calc_map) { // 计算mAP。
......
net_map = parse_network_cfg_custom(cfgfile, 1, 1); // parser.c中parse_network_cfg_custom函数入口,加载cfg和参数构建网络,batch = 1。
net_map.benchmark_layers = benchmark_layers;
const int net_classes = net_map.layers[net_map.n - 1].classes;
int k; // free memory unnecessary arrays
for (k = 0; k < net_map.n - 1; ++k) free_layer_custom(net_map.layers[k], 1);
......
}
srand(time(0));
char *base = basecfg(cfgfile); // utils.c中basecfg()函数入口,解析cfg/yolo-obj.cfg文件,就是模型的配置参数,并打印。
printf("%s\n", base);
float avg_loss = -1;
network* nets = (network*)xcalloc(ngpus, sizeof(network)); // 给network结构体分内存,用来储存网络参数。
srand(time(0));
int seed = rand();
int k;
for (k = 0; k < ngpus; ++k) {
srand(seed);
#ifdef GPU
cuda_set_device(gpus[k]);
#endif
nets[k] = parse_network_cfg(cfgfile); // parse_network_cfg_custom(cfgfile, 0, 0),nets根据GPU个数分别加载配置文件。
nets[k].benchmark_layers = benchmark_layers;
if (weightfile) {
load_weights(&nets[k], weightfile); // parser.c中load_weights()接口,读取权重文件。
}
if (clear) { // 是否清零。
*nets[k].seen = 0;
*nets[k].cur_iteration = 0;
}
nets[k].learning_rate *= ngpus;
}
srand(time(0));
network net = nets[0]; // 参数传递给net
......
/* 准备加载参数。 */
load_args args = { 0 };
args.w = net.w;
args.h = net.h;
args.c = net.c;
args.paths = paths;
args.n = imgs;
args.m = plist->size;
args.classes = classes;
args.flip = net.flip;
args.jitter = l.jitter;
args.resize = l.resize;
args.num_boxes = l.max_boxes;
net.num_boxes = args.num_boxes;
net.train_images_num = train_images_num;
args.d = &buffer;
args.type = DETECTION_DATA;
args.threads = 64; // 16 or 64
......
“darknet/src/parser.c”–parse_network_cfg_custom()函数中:
network parse_network_cfg_custom(char *filename, int batch, int time_steps)
{
list *sections = read_cfg(filename); // 读取配置文件,构建成一个链表list。
node *n = sections->front; // 定义sections的首节点为n。
if(!n) error("Config file has no sections");
network net = make_network(sections->size - 1); // network.c中,make_network函数入口,从net变量下一层开始,依次为其中的指针变量分配内存。由于第一个段[net]中存放的是和网络并不直接相关的配置参数,因此网络中层的数目为sections->size - 1。
net.gpu_index = gpu_index;
size_params params;
if (batch > 0) params.train = 0; // allocates memory for Detection only
else params.train = 1; // allocates memory for Detection & Training
section *s = (section *)n->val; // 首节点n的val传递给section。
list *options = s->options;
if(!is_network(s)) error("First section must be [net] or [network]");
parse_net_options(options, &net); // 初始化网络全局参数,包含但不限于[net]中的参数。
#ifdef GPU
printf("net.optimized_memory = %d \n", net.optimized_memory);
if (net.optimized_memory >= 2 && params.train) {
pre_allocate_pinned_memory((size_t)1024 * 1024 * 1024 * 8); // pre-allocate 8 GB CPU-RAM for pinned memory
}
#endif // GPU
......
while(n){ //初始化每一层的参数。
params.index = count;
fprintf(stderr, "%4d ", count);
s = (section *)n->val;
options = s->options;
layer l = { (LAYER_TYPE)0 };
LAYER_TYPE lt = string_to_layer_type(s->type);
if(lt == CONVOLUTIONAL){ // 卷积层,调用parse_convolutional()函数执行make_convolutional_layer()创建卷积层。
l = parse_convolutional(options, params);
}else if(lt == LOCAL){
l = parse_local(options, params);
}else if(lt == ACTIVE){
l = parse_activation(options, params);
}else if(lt == RNN){
l = parse_rnn(options, params);
}else if(lt == GRU){
l = parse_gru(options, params);
}else if(lt == LSTM){
l = parse_lstm(options, params);
}else if (lt == CONV_LSTM) {
l = parse_conv_lstm(options, params);
}else if(lt == CRNN){
l = parse_crnn(options, params);
}else if(lt == CONNECTED){
l = parse_connected(options, params);
}else if(lt == CROP){
l = parse_crop(options, params);
}else if(lt == COST){
l = parse_cost(options, params);
l.keep_delta_gpu = 1;
}else if(lt == REGION){
l = parse_region(options, params);
l.keep_delta_gpu = 1;
}else if (lt == YOLO) { // yolov3/4引入的yolo_layer,调用parse_yolo()函数执行make_yolo_layer()创建yolo层。
l = parse_yolo(options, params);
l.keep_delta_gpu = 1;
}else if (lt == GAUSSIAN_YOLO) {
l = parse_gaussian_yolo(options, params);
l.keep_delta_gpu = 1;
}else if(lt == DETECTION){
l = parse_detection(options, params);
}else if(lt == SOFTMAX){
l = parse_softmax(options, params);
net.hierarchy = l.softmax_tree;
l.keep_delta_gpu = 1;
}else if(lt == NORMALIZATION){
l = parse_normalization(options, params);
}else if(lt == BATCHNORM){
l = parse_batchnorm(options, params);
}else if(lt == MAXPOOL){
l = parse_maxpool(options, params);
}else if (lt == LOCAL_AVGPOOL) {
l = parse_local_avgpool(options, params);
}else if(lt == REORG){
l = parse_reorg(options, params); }
else if (lt == REORG_OLD) {
l = parse_reorg_old(options, params);
}else if(lt == AVGPOOL){
l = parse_avgpool(options, params);
}else if(lt == ROUTE){
l = parse_route(options, params);
int k;
for (k = 0; k < l.n; ++k) {
net.layers[l.input_layers[k]].use_bin_output = 0;
net.layers[l.input_layers[k]].keep_delta_gpu = 1;
}
}else if (lt == UPSAMPLE) {
l = parse_upsample(options, params, net);
}else if(lt == SHORTCUT){
l = parse_shortcut(options, params, net);
net.layers[count - 1].use_bin_output = 0;
net.layers[l.index].use_bin_output = 0;
net.layers[l.index].keep_delta_gpu = 1;
}else if (lt == SCALE_CHANNELS) {
l = parse_scale_channels(options, params, net);
net.layers[count - 1].use_bin_output = 0;
net.layers[l.index].use_bin_output = 0;
net.layers[l.index].keep_delta_gpu = 1;
}
else if (lt == SAM) {
l = parse_sam(options, params, net);
net.layers[count - 1].use_bin_output = 0;
net.layers[l.index].use_bin_output = 0;
net.layers[l.index].keep_delta_gpu = 1;
}else if(lt == DROPOUT){
l = parse_dropout(options, params);
l.output = net.layers[count-1].output;
l.delta = net.layers[count-1].delta;
#ifdef GPU
l.output_gpu = net.layers[count-1].output_gpu;
l.delta_gpu = net.layers[count-1].delta_gpu;
l.keep_delta_gpu = 1;
#endif
}
else if (lt == EMPTY) {
layer empty_layer = {(LAYER_TYPE)0};
empty_layer.out_w = params.w;
empty_layer.out_h = params.h;
empty_layer.out_c = params.c;
l = empty_layer;
l.output = net.layers[count - 1].output;
l.delta = net.layers[count - 1].delta;
#ifdef GPU
l.output_gpu = net.layers[count - 1].output_gpu;
l.delta_gpu = net.layers[count - 1].delta_gpu;
#endif
}else{
fprintf(stderr, "Type not recognized: %s\n", s->type);
}
......
net.layers[count] = l; // 每个解析函数返回一个填充好的层l,将这些层全部添加到network结构体的layers数组中。
if (l.workspace_size > workspace_size) workspace_size = l.workspace_size; // workspace_size表示网络的工作空间,指的是所有层中占用运算空间最大的那个层的,因为实际上在GPU或CPU中某个时刻只有一个层在做前向或反向运算。
if (l.inputs > max_inputs) max_inputs = l.inputs;
if (l.outputs > max_outputs) max_outputs = l.outputs;
free_section(s);
n = n->next; // node节点前沿,empty则while-loop结束。
++count;
if(n){ // 这部分将连接的两个层之间的输入输出shape统一。
if (l.antialiasing) {
params.h = l.input_layer->out_h;
params.w = l.input_layer->out_w;
params.c = l.input_layer->out_c;
params.inputs = l.input_layer->outputs;
}
else {
params.h = l.out_h;
params.w = l.out_w;
params.c = l.out_c;
params.inputs = l.outputs;
}
}
if (l.bflops > 0) bflops += l.bflops;
if (l.w > 1 && l.h > 1) {
avg_outputs += l.outputs;
avg_counter++;
}
}
free_list(sections);
......
return net; // 返回解析好的network类型的指针变量,这个指针变量会伴随训练的整个过程。
}
以卷积层和yolo层为例,介绍网络层的创建过程,convolutional_layer.c中make_convolutional_layer()函数:
convolutional_layer make_convolutional_layer(int batch, int steps, int h, int w, int c, int n, int groups, int size, int stride_x, int stride_y, int dilation, int padding, ACTIVATION activation, int batch_normalize, int binary, int xnor, int adam, int use_bin_output, int index, int antialiasing, convolutional_layer *share_layer, int assisted_excitation, int deform, int train)
{
int total_batch = batch*steps;
int i;
convolutional_layer l = { (LAYER_TYPE)0 }; // convolutional_layer其实就是layer。
l.type = CONVOLUTIONAL; // layer的类型,此处为卷积层。
l.train = train;
/* 改变输入和输出的维度。 */
if (xnor) groups = 1; // disable groups for XNOR-net
if (groups < 1) groups = 1; // group将对应的输入输出通道对应分组,默认为1(输出输入的所有通道各为一组),把卷积group等于输入通道,输出通道等于输入通道就实现了depthwize separable convolution结构。
const int blur_stride_x = stride_x;
const int blur_stride_y = stride_y;
l.antialiasing = antialiasing;
if (antialiasing) {
stride_x = stride_y = l.stride = l.stride_x = l.stride_y = 1; // use stride=1 in host-layer
}
l.deform = deform;
l.assisted_excitation = assisted_excitation;
l.share_layer = share_layer;
l.index = index;
l.h = h; // input的高。
l.w = w; // input的宽。
l.c = c; // input的通道。
l.groups = groups;
l.n = n; // 卷积核filter的个数。
l.binary = binary;
l.xnor = xnor;
l.use_bin_output = use_bin_output;
l.batch = batch; // 训练使用的batch_size。
l.steps = steps;
l.stride = stride_x; // 移动步长。
l.stride_x = stride_x;
l.stride_y = stride_y;
l.dilation = dilation;
l.size = size; // 卷积核的大小。
l.pad = padding; // 边界填充宽度。
l.batch_normalize = batch_normalize; // 是否进行BN操作。
l.learning_rate_scale = 1;
/* 数组的大小: c/groups*n*size*size。 */
l.nweights = (c / groups) * n * size * size; // groups默认值为1,出现c的原因是对多个通道的广播操作。
if (l.share_layer) {
if (l.size != l.share_layer->size || l.nweights != l.share_layer->nweights || l.c != l.share_layer->c || l.n != l.share_layer->n) {
printf(" Layer size, nweights, channels or filters don't match for the share_layer");
getchar();
}
l.weights = l.share_layer->weights;
l.weight_updates = l.share_layer->weight_updates;
l.biases = l.share_layer->biases;
l.bias_updates = l.share_layer->bias_updates;
}
else {
l.weights = (float*)xcalloc(l.nweights, sizeof(float));
l.biases = (float*)xcalloc(n, sizeof(float));
if (train) {
l.weight_updates = (float*)xcalloc(l.nweights, sizeof(float));
l.bias_updates = (float*)xcalloc(n, sizeof(float));
}
}
// float scale = 1./sqrt(size*size*c);
float scale = sqrt(2./(size*size*c/groups)); // 初始值scale。
if (l.activation == NORM_CHAN || l.activation == NORM_CHAN_SOFTMAX || l.activation == NORM_CHAN_SOFTMAX_MAXVAL) {
for (i = 0; i < l.nweights; ++i) l.weights[i] = 1; // rand_normal();
}
else {
for (i = 0; i < l.nweights; ++i) l.weights[i] = scale*rand_uniform(-1, 1); // rand_normal();
}
/* 根据公式计算输出维度。 */
int out_h = convolutional_out_height(l);
int out_w = convolutional_out_width(l);
l.out_h = out_h; // output的高。
l.out_w = out_w; // output的宽。
l.out_c = n; // output的通道,等于卷积核个数。
l.outputs = l.out_h * l.out_w * l.out_c; // 一个batch的output维度大小。
l.inputs = l.w * l.h * l.c; // 一个batch的input维度大小。
l.activation = activation;
l.output = (float*)xcalloc(total_batch*l.outputs, sizeof(float)); // 输出数组。
#ifndef GPU
if (train) l.delta = (float*)xcalloc(total_batch*l.outputs, sizeof(float)); // 暂存更新数据的输出数组。
#endif // not GPU
/* 三个重要的函数,前向运算,反向传播和更新函数。 */
l.forward = forward_convolutional_layer;
l.backward = backward_convolutional_layer;
l.update = update_convolutional_layer; // 明确了更新的策略。
if(binary){
l.binary_weights = (float*)xcalloc(l.nweights, sizeof(float));
l.cweights = (char*)xcalloc(l.nweights, sizeof(char));
l.scales = (float*)xcalloc(n, sizeof(float));
}
if(xnor){
l.binary_weights = (float*)xcalloc(l.nweights, sizeof(float));
l.binary_input = (float*)xcalloc(l.inputs * l.batch, sizeof(float));
int align = 32;// 8;
int src_align = l.out_h*l.out_w;
l.bit_align = src_align + (align - src_align % align);
l.mean_arr = (float*)xcalloc(l.n, sizeof(float));
const size_t new_c = l.c / 32;
size_t in_re_packed_input_size = new_c * l.w * l.h + 1;
l.bin_re_packed_input = (uint32_t*)xcalloc(in_re_packed_input_size, sizeof(uint32_t));
l.lda_align = 256; // AVX2
int k = l.size*l.size*l.c;
size_t k_aligned = k + (l.lda_align - k%l.lda_align);
size_t t_bit_input_size = k_aligned * l.bit_align / 8;
l.t_bit_input = (char*)xcalloc(t_bit_input_size, sizeof(char));
}
/* Batch Normalization相关的变量设置。 */
if(batch_normalize){
if (l.share_layer) {
l.scales = l.share_layer->scales;
l.scale_updates = l.share_layer->scale_updates;
l.mean = l.share_layer->mean;
l.variance = l.share_layer->variance;
l.mean_delta = l.share_layer->mean_delta;
l.variance_delta = l.share_layer->variance_delta;
l.rolling_mean = l.share_layer->rolling_mean;
l.rolling_variance = l.share_layer->rolling_variance;
}
else {
l.scales = (float*)xcalloc(n, sizeof(float));
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
l.scales[i] = 1;
}
if (train) {
l.scale_updates = (float*)xcalloc(n, sizeof(float));
l.mean = (float*)xcalloc(n, sizeof(float));
l.variance = (float*)xcalloc(n, sizeof(float));
l.mean_delta = (float*)xcalloc(n, sizeof(float));
l.variance_delta = (float*)xcalloc(n, sizeof(float));
}
l.rolling_mean = (float*)xcalloc(n, sizeof(float));
l.rolling_variance = (float*)xcalloc(n, sizeof(float));
}
......
return l;
}
yolo_layer.c中make_yolo_layer()函数:
layer make_yolo_layer(int batch, int w, int h, int n, int total, int *mask, int classes, int max_boxes)
{
int i;
layer l = { (LAYER_TYPE)0 };
l.type = YOLO; // 层类别。
l.n = n; // 一个cell能预测多少个b-box。
l.total = total; // anchors数目,9。
l.batch = batch; // 一个batch包含的图像张数。
l.h = h; // input的高。
l.w = w; // imput的宽。
l.c = n*(classes + 4 + 1);
l.out_w = l.w; // output的高。
l.out_h = l.h; // output的宽。
l.out_c = l.c; // output的通道,等于卷积核个数。
l.classes = classes; // 目标类别数。
l.cost = (float*)xcalloc(1, sizeof(float)); // yolo层总的损失。
l.biases = (float*)xcalloc(total * 2, sizeof(float)); // 储存b-box的anchor box的[w,h]。
if(mask) l.mask = mask; // 有mask传入。
else{
l.mask = (int*)xcalloc(n, sizeof(int));
for(i = 0; i < n; ++i){
l.mask[i] = i;
}
}
l.bias_updates = (float*)xcalloc(n * 2, sizeof(float)); // 储存b-box的anchor box的[w,h]的更新值。
l.outputs = h*w*n*(classes + 4 + 1); // 一张训练图片经过yolo层后得到的输出元素个数(Grid数*每个Grid预测的矩形框数*每个矩形框的参数个数)
l.inputs = l.outputs; // 一张训练图片输入到yolo层的元素个数(对于yolo_layer,输入和输出的元素个数相等)
l.max_boxes = max_boxes; // 一张图片最多有max_boxes个ground truth矩形框,这个数量时固定写死的。
l.truths = l.max_boxes*(4 + 1); // 4个定位参数+1个物体类别,大于GT实际参数数量。
l.delta = (float*)xcalloc(batch * l.outputs, sizeof(float)); // yolo层误差项,包含整个batch的。
l.output = (float*)xcalloc(batch * l.outputs, sizeof(float)); // yolo层所有输出,包含整个batch的。
/* 存储b-box的Anchor box的[w,h]的初始化,在parse.c中parse_yolo函数会加载cfg中Anchor尺寸。*/
for(i = 0; i < total*2; ++i){
l.biases[i] = .5;
}
/* 前向运算,反向传播函数。*/
l.forward = forward_yolo_layer;
l.backward = backward_yolo_layer;
#ifdef GPU
l.forward_gpu = forward_yolo_layer_gpu;
l.backward_gpu = backward_yolo_layer_gpu;
l.output_gpu = cuda_make_array(l.output, batch*l.outputs);
l.output_avg_gpu = cuda_make_array(l.output, batch*l.outputs);
l.delta_gpu = cuda_make_array(l.delta, batch*l.outputs);
free(l.output);
if (cudaSuccess == cudaHostAlloc(&l.output, batch*l.outputs*sizeof(float), cudaHostRegisterMapped)) l.output_pinned = 1;
else {
cudaGetLastError(); // reset CUDA-error
l.output = (float*)xcalloc(batch * l.outputs, sizeof(float));
}
free(l.delta);
if (cudaSuccess == cudaHostAlloc(&l.delta, batch*l.outputs*sizeof(float), cudaHostRegisterMapped)) l.delta_pinned = 1;
else {
cudaGetLastError(); // reset CUDA-error
l.delta = (float*)xcalloc(batch * l.outputs, sizeof(float));
}
#endif
fprintf(stderr, "yolo\n");
srand(time(0));
return l;
}
这里要强调下”darknet/src/list.h”中定义的数据结构list:
typedef struct node{
void *val;
struct node *next;
struct node *prev;
} node;
typedef struct list{
int size; // list的所有节点个数。
node *front; // list的首节点。
node *back; // list的普通节点。
} list; // list类型变量保存所有的网络参数,有很多的sections节点,每个section中又有一个保存层参数的小list。
以及”darknet/src/parser.c”中定义的数据结构section:
typedef struct{
char *type; // section的类型,保存的是网络中每一层的网络类型和参数。在.cfg配置文件中, 以‘[’开头的行被称为一个section(段)。
list *options; // section的参数信息。
}section;
“darknet/src/parser.c”–read_cfg()函数的作用就是读取.cfg配置文件并返回给list类型变量sections:
/* 读取神经网络结构配置文件.cfg文件中的配置数据,将每个神经网络层参数读取到每个section结构体(每个section是sections的一个节点)中,而后全部插入到list结构体sections中并返回。*/
/* param: filename是C风格字符数组,神经网络结构配置文件路径。*/
/* return: list结构体指针,包含从神经网络结构配置文件中读入的所有神经网络层的参数。*/
list *read_cfg(char *filename)
{
FILE *file = fopen(filename, "r");
if(file == 0) file_error(filename);
/* 一个section表示配置文件中的一个字段,也就是网络结构中的一层,因此,一个section将读取并存储某一层的参数以及该层的type。 */
char *line;
int nu = 0; // 当前读取行记号。
list *sections = make_list(); // sections包含所有的神经网络层参数。
section *current = 0; // 当前读取到的某一层。
while((line=fgetl(file)) != 0){
++ nu;
strip(line); // 去除读入行中含有的空格符。
switch(line[0]){
/* 以'['开头的行是一个新的section,其内容是层的type,比如[net],[maxpool],[convolutional]... */
case '[':
current = (section*)xmalloc(sizeof(section)); // 读到了一个新的section:current。
list_insert(sections, current); // list.c中,list_insert函数入口,将该新的section保存起来。
current->options = make_list();
current->type = line;
break;
case '\0': // 空行。
case '#': // 注释。
case ';': // 空行。
free(line); // 对于上述三种情况直接释放内存即可。
break;
/* 剩下的才真正是网络结构的数据,调用read_option()函数读取,返回0说明文件中的数据格式有问题,将会提示错误。 */
default:
if(!read_option(line, current->options)){ // 将读取到的参数保存在current变量的options中,这里保存在options节点中的数据为kvp键值对类型。
fprintf(stderr, "Config file error line %d, could parse: %s\n", nu, line);
free(line);
}
break;
}
}
fclose(file);
return sections;
}
综上,解析过程将链表中的网络参数保存到network结构体,用于后续权重更新。
六. 权重更新
“darknet/src/detector.c”–train_detector()函数中:
......
/* 开始训练网络 */
float loss = 0;
#ifdef GPU
if (ngpus == 1) {
int wait_key = (dont_show) ? 0 : 1;
loss = train_network_waitkey(net, train, wait_key); // network.c中,train_network_waitkey函数入口,分配内存并执行网络训练。
}
else {
loss = train_networks(nets, ngpus, train, 4); // network_kernels.cu中,train_networks函数入口,多GPU训练。
}
#else
loss = train_network(net, train); // train_network_waitkey(net, d, 0),CPU模式。
#endif
if (avg_loss < 0 || avg_loss != avg_loss) avg_loss = loss; // if(-inf or nan)
avg_loss = avg_loss*.9 + loss*.1;
......
以CPU训练为例,”darknet/src/network.c”–train_network()函数,执行train_network_waitkey(net, d, 0):
float train_network_waitkey(network net, data d, int wait_key)
{
assert(d.X.rows % net.batch == 0);
int batch = net.batch; // detector.c中train_detector函数在nets[k] = parse_network_cfg(cfgfile)处调用parser.c中的parse_net_options函数,有net->batch /= subdivs,所以batch_size = batch/subdivisions。
int n = d.X.rows / batch; // batch个数, 对于单GPU和CPU,n = subdivision。
float* X = (float*)xcalloc(batch * d.X.cols, sizeof(float));
float* y = (float*)xcalloc(batch * d.y.cols, sizeof(float));
int i;
float sum = 0;
for(i = 0; i < n; ++i){
get_next_batch(d, batch, i*batch, X, y);
net.current_subdivision = i;
float err = train_network_datum(net, X, y); // 调用train_network_datum函数得到误差Loss。
sum += err;
if(wait_key) wait_key_cv(5);
}
(*net.cur_iteration) += 1;
#ifdef GPU
update_network_gpu(net);
#else // GPU
update_network(net);
#endif // GPU
free(X);
free(y);
return (float)sum/(n*batch);
}
其中,调用train_network_datum()函数计算error是核心:
float train_network_datum(network net, float *x, float *y)
{
#ifdef GPU
if(gpu_index >= 0) return train_network_datum_gpu(net, x, y); // GPU模式,调用network_kernels.cu中train_network_datum_gpu函数。
#endif
network_state state={0};
*net.seen += net.batch;
state.index = 0;
state.net = net;
state.input = x;
state.delta = 0;
state.truth = y;
state.train = 1;
forward_network(net, state); // CPU模式,正向传播。
backward_network(net, state); // CPU模式,BP。
float error = get_network_cost(net); // 计算Loss。
return error;
}
进一步分析forward_network()函数:
void forward_network(network net, network_state state)
{
state.workspace = net.workspace;
int i;
for(i = 0; i < net.n; ++i){
state.index = i;
layer l = net.layers[i];
if(l.delta && state.train){
scal_cpu(l.outputs * l.batch, 0, l.delta, 1); // blas.c中,scal_cpu函数入口。
}
l.forward(l, state); // 不同层l.forward代表不同函数,如:convolutional_layer.c中,l.forward = forward_convolutional_layer;yolo_layer.c中,l.forward = forward_yolo_layer,CPU执行前向运算。
state.input = l.output; // 上一层的输出传递给下一层的输入。
}
}
卷积层时,forward_convolutional_layer()函数:
void forward_convolutional_layer(convolutional_layer l, network_state state)
{
/* 获取卷积层输出的长宽。*/
int out_h = convolutional_out_height(l);
int out_w = convolutional_out_width(l);
int i, j;
fill_cpu(l.outputs*l.batch, 0, l.output, 1); // 把output初始化为0。
/* xnor-net,将inputs和weights二值化。*/
if (l.xnor && (!l.align_bit_weights || state.train)) {
if (!l.align_bit_weights || state.train) {
binarize_weights(l.weights, l.n, l.nweights, l.binary_weights);
}
swap_binary(&l);
binarize_cpu(state.input, l.c*l.h*l.w*l.batch, l.binary_input);
state.input = l.binary_input;
}
/* m是卷积核的个数,k是每个卷积核的参数数量(l.size是卷积核的大小),n是每个输出feature map的像素个数。*/
int m = l.n / l.groups;
int k = l.size*l.size*l.c / l.groups;
int n = out_h*out_w;
static int u = 0;
u++;
for(i = 0; i < l.batch; ++i)
{
for (j = 0; j < l.groups; ++j)
{
/* weights是卷积核的参数,a是指向权重的指针,b是指向工作空间指针,c是指向输出的指针。*/
float *a = l.weights +j*l.nweights / l.groups;
float *b = state.workspace;
float *c = l.output +(i*l.groups + j)*n*m;
if (l.xnor && l.align_bit_weights && !state.train && l.stride_x == l.stride_y)
{
memset(b, 0, l.bit_align*l.size*l.size*l.c * sizeof(float));
if (l.c % 32 == 0)
{
int ldb_align = l.lda_align;
size_t new_ldb = k + (ldb_align - k%ldb_align); // (k / 8 + 1) * 8;
int re_packed_input_size = l.c * l.w * l.h;
memset(state.workspace, 0, re_packed_input_size * sizeof(float));
const size_t new_c = l.c / 32;
size_t in_re_packed_input_size = new_c * l.w * l.h + 1;
memset(l.bin_re_packed_input, 0, in_re_packed_input_size * sizeof(uint32_t));
// float32x4 by channel (as in cuDNN)
repack_input(state.input, state.workspace, l.w, l.h, l.c);
// 32 x floats -> 1 x uint32_t
float_to_bit(state.workspace, (unsigned char *)l.bin_re_packed_input, l.c * l.w * l.h);
/* image to column,就是将图像依照卷积核的大小拉伸为列向量,方便矩阵运算,将图像每一个kernel转换成一列。*/
im2col_cpu_custom((float *)l.bin_re_packed_input, new_c, l.h, l.w, l.size, l.stride, l.pad, state.workspace);
int new_k = l.size*l.size*l.c / 32;
transpose_uint32((uint32_t *)state.workspace, (uint32_t*)l.t_bit_input, new_k, n, n, new_ldb);
/* General Matrix Multiply函数,实现矩阵运算,也就是卷积运算。*/
gemm_nn_custom_bin_mean_transposed(m, n, k, 1, (unsigned char*)l.align_bit_weights, new_ldb, (unsigned char*)l.t_bit_input, new_ldb, c, n, l.mean_arr);
}
else
{
im2col_cpu_custom_bin(state.input, l.c, l.h, l.w, l.size, l.stride, l.pad, state.workspace, l.bit_align);
// transpose B from NxK to KxN (x-axis (ldb = l.size*l.size*l.c) - should be multiple of 8 bits)
{
int ldb_align = l.lda_align;
size_t new_ldb = k + (ldb_align - k%ldb_align);
size_t t_intput_size = binary_transpose_align_input(k, n, state.workspace, &l.t_bit_input, ldb_align, l.bit_align);
// 5x times faster than gemm()-float32
gemm_nn_custom_bin_mean_transposed(m, n, k, 1, (unsigned char*)l.align_bit_weights, new_ldb, (unsigned char*)l.t_bit_input, new_ldb, c, n, l.mean_arr);
}
}
add_bias(l.output, l.biases, l.batch, l.n, out_h*out_w); //添加偏移项。
/* 非线性变化,leaky RELU、Mish等激活函数。*/
if (l.activation == SWISH) activate_array_swish(l.output, l.outputs*l.batch, l.activation_input, l.output);
else if (l.activation == MISH) activate_array_mish(l.output, l.outputs*l.batch, l.activation_input, l.output);
else if (l.activation == NORM_CHAN) activate_array_normalize_channels(l.output, l.outputs*l.batch, l.batch, l.out_c, l.out_w*l.out_h, l.output);
else if (l.activation == NORM_CHAN_SOFTMAX) activate_array_normalize_channels_softmax(l.output, l.outputs*l.batch, l.batch, l.out_c, l.out_w*l.out_h, l.output, 0);
else if (l.activation == NORM_CHAN_SOFTMAX_MAXVAL) activate_array_normalize_channels_softmax(l.output, l.outputs*l.batch, l.batch, l.out_c, l.out_w*l.out_h, l.output, 1);
else activate_array_cpu_custom(l.output, m*n*l.batch, l.activation);
return;
}
else {
float *im = state.input + (i*l.groups + j)*(l.c / l.groups)*l.h*l.w;
if (l.size == 1) {
b = im;
}
else {
im2col_cpu_ext(im, // input
l.c / l.groups, // input channels
l.h, l.w, // input size (h, w)
l.size, l.size, // kernel size (h, w)
l.pad * l.dilation, l.pad * l.dilation, // padding (h, w)
l.stride_y, l.stride_x, // stride (h, w)
l.dilation, l.dilation, // dilation (h, w)
b); // output
}
gemm(0, 0, m, n, k, 1, a, k, b, n, 1, c, n);
// bit-count to float
}
}
}
if(l.batch_normalize){ // BN层,加速收敛。
forward_batchnorm_layer(l, state);
}
else { // 直接加上bias,output += bias。
add_bias(l.output, l.biases, l.batch, l.n, out_h*out_w);
}
/* 非线性变化,leaky RELU、Mish等激活函数。*/
if (l.activation == SWISH) activate_array_swish(l.output, l.outputs*l.batch, l.activation_input, l.output);
else if (l.activation == MISH) activate_array_mish(l.output, l.outputs*l.batch, l.activation_input, l.output);
else if (l.activation == NORM_CHAN) activate_array_normalize_channels(l.output, l.outputs*l.batch, l.batch, l.out_c, l.out_w*l.out_h, l.output);
else if (l.activation == NORM_CHAN_SOFTMAX) activate_array_normalize_channels_softmax(l.output, l.outputs*l.batch, l.batch, l.out_c, l.out_w*l.out_h, l.output, 0);
else if (l.activation == NORM_CHAN_SOFTMAX_MAXVAL) activate_array_normalize_channels_softmax(l.output, l.outputs*l.batch, l.batch, l.out_c, l.out_w*l.out_h, l.output, 1);
else activate_array_cpu_custom(l.output, l.outputs*l.batch, l.activation);
if(l.binary || l.xnor) swap_binary(&l); // 二值化。
if(l.assisted_excitation && state.train) assisted_excitation_forward(l, state);
if (l.antialiasing) {
network_state s = { 0 };
s.train = state.train;
s.workspace = state.workspace;
s.net = state.net;
s.input = l.output;
forward_convolutional_layer(*(l.input_layer), s);
memcpy(l.output, l.input_layer->output, l.input_layer->outputs * l.input_layer->batch * sizeof(float));
}
}
yolo层时,forward_yolo_layer()函数:
void forward_yolo_layer(const layer l, network_state state)
{
int i, j, b, t, n;
memcpy(l.output, state.input, l.outputs*l.batch * sizeof(float)); // 将层输入直接copy到层输出。
/* 在cpu模式,把预测输出的x,y,confidence和所有类别都sigmoid激活,确保值在0~1之间。*/
#ifndef GPU
for (b = 0; b < l.batch; ++b) {
for (n = 0; n < l.n; ++n) {
int index = entry_index(l, b, n*l.w*l.h, 0); // 获取第b个batch开始的index。
/* 对预测的tx,ty进行逻辑回归。*/
activate_array(l.output + index, 2 * l.w*l.h, LOGISTIC); // x,y,
scal_add_cpu(2 * l.w*l.h, l.scale_x_y, -0.5*(l.scale_x_y - 1), l.output + index, 1); // scale x,y
index = entry_index(l, b, n*l.w*l.h, 4); // 获取第b个batch confidence开始的index。
activate_array(l.output + index, (1 + l.classes)*l.w*l.h, LOGISTIC); // 对预测的confidence以及class进行逻辑回归。
}
}
#endif
// delta is zeroed
memset(l.delta, 0, l.outputs * l.batch * sizeof(float)); // 将yolo层的误差项进行初始化(包含整个batch的)。
if (!state.train) return; // 不是训练阶段,return。
float tot_iou = 0; // 总的IOU。
float tot_giou = 0;
float tot_diou = 0;
float tot_ciou = 0;
float tot_iou_loss = 0;
float tot_giou_loss = 0;
float tot_diou_loss = 0;
float tot_ciou_loss = 0;
float recall = 0;
float recall75 = 0;
float avg_cat = 0;
float avg_obj = 0;
float avg_anyobj = 0;
int count = 0;
int class_count = 0;
*(l.cost) = 0; // yolo层的总损失初始化为0。
for (b = 0; b < l.batch; ++b) { // 遍历batch中的每一张图片。
for (j = 0; j < l.h; ++j) {
for (i = 0; i < l.w; ++i) { // 遍历每个Grid cell, 当前cell编号[j, i]。
for (n = 0; n < l.n; ++n) { // 遍历每一个bbox,当前bbox编号[n]。
const int class_index = entry_index(l, b, n*l.w*l.h + j*l.w + i, 4 + 1); // 预测b-box类别s下标。 const int obj_index = entry_index(l, b, n*l.w*l.h + j*l.w + i, 4); // 预测b-box objectness下标。
const int box_index = entry_index(l, b, n*l.w*l.h + j*l.w + i, 0); // 获得第j*w+i个cell第n个b-box的index。
const int stride = l.w*l.h;
/* 计算第j*w+i个cell第n个b-box在当前特征图上的相对位置[x,y],在网络输入图片上的相对宽度、高度[w,h]。*/
box pred = get_yolo_box(l.output, l.biases, l.mask[n], box_index, i, j, l.w, l.h, state.net.w, state.net.h, l.w*l.h);
float best_match_iou = 0;
int best_match_t = 0;
float best_iou = 0; // 保存最大IOU。
int best_t = 0; // 保存最大IOU的bbox id。
for (t = 0; t < l.max_boxes; ++t) { // 遍历每一个GT bbox。
box truth = float_to_box_stride(state.truth + t*(4 + 1) + b*l.truths, 1); // 将第t个bbox由float数组转bbox结构体,方便计算IOU。
int class_id = state.truth[t*(4 + 1) + b*l.truths + 4]; // 获取第t个bbox的类别,检查是否有标注错误。
if (class_id >= l.classes || class_id < 0) {
printf("\n Warning: in txt-labels class_id=%d >= classes=%d in cfg-file. In txt-labels class_id should be [from 0 to %d] \n", class_id, l.classes, l.classes - 1);
printf("\n truth.x = %f, truth.y = %f, truth.w = %f, truth.h = %f, class_id = %d \n", truth.x, truth.y, truth.w, truth.h, class_id);
if (check_mistakes) getchar();
continue; // if label contains class_id more than number of classes in the cfg-file and class_id check garbage value
}
if (!truth.x) break; // 如果x坐标为0则break,因为定义了max_boxes个b-box。
float objectness = l.output[obj_index]; // 预测bbox object置信度。
if (isnan(objectness) || isinf(objectness)) l.output[obj_index] = 0;
/* 获得预测b-box的类别信息,如果某个类别的概率超过0.25返回1。*/
int class_id_match = compare_yolo_class(l.output, l.classes, class_index, l.w*l.h, objectness, class_id, 0.25f);
float iou = box_iou(pred, truth); // 计算pred b-box与第t个GT bbox之间的IOU。
if (iou > best_match_iou && class_id_match == 1) { // class_id_match=1的限制,即预测b-box的置信度必须大于0.25。
best_match_iou = iou;
best_match_t = t;
}
if (iou > best_iou) {
best_iou = iou; // 更新最大的IOU。
best_t = t; // 记录该GT b-box的编号t。
}
}
avg_anyobj += l.output[obj_index]; // 统计pred b-box的confidence。
l.delta[obj_index] = l.cls_normalizer * (0 - l.output[obj_index]); // 将所有pred b-box都当做noobject, 计算其confidence梯度,cls_normalizer是平衡系数。
if (best_match_iou > l.ignore_thresh) { // best_iou大于阈值则说明pred box有物体。
const float iou_multiplier = best_match_iou*best_match_iou;// (best_match_iou - l.ignore_thresh) / (1.0 - l.ignore_thresh);
if (l.objectness_smooth) {
l.delta[obj_index] = l.cls_normalizer * (iou_multiplier - l.output[obj_index]);
int class_id = state.truth[best_match_t*(4 + 1) + b*l.truths + 4];
if (l.map) class_id = l.map[class_id];
const float class_multiplier = (l.classes_multipliers) ? l.classes_multipliers[class_id] : 1.0f;
l.delta[class_index + stride*class_id] = class_multiplier * (iou_multiplier - l.output[class_index + stride*class_id]);
}
else l.delta[obj_index] = 0;
}
else if (state.net.adversarial) { // 自对抗训练。
int stride = l.w*l.h;
float scale = pred.w * pred.h;
if (scale > 0) scale = sqrt(scale);
l.delta[obj_index] = scale * l.cls_normalizer * (0 - l.output[obj_index]);
int cl_id;
for (cl_id = 0; cl_id < l.classes; ++cl_id) {
if(l.output[class_index + stride*cl_id] * l.output[obj_index] > 0.25)
l.delta[class_index + stride*cl_id] = scale * (0 - l.output[class_index + stride*cl_id]);
}
}
if (best_iou > l.truth_thresh) { // pred b-box为完全预测正确样本,cfg中truth_thresh=1,语句永远不可能成立。
const float iou_multiplier = best_iou*best_iou;// (best_iou - l.truth_thresh) / (1.0 - l.truth_thresh);
if (l.objectness_smooth) l.delta[obj_index] = l.cls_normalizer * (iou_multiplier - l.output[obj_index]);
else l.delta[obj_index] = l.cls_normalizer * (1 - l.output[obj_index]);
int class_id = state.truth[best_t*(4 + 1) + b*l.truths + 4];
if (l.map) class_id = l.map[class_id];
delta_yolo_class(l.output, l.delta, class_index, class_id, l.classes, l.w*l.h, 0, l.focal_loss, l.label_smooth_eps, l.classes_multipliers);
const float class_multiplier = (l.classes_multipliers) ? l.classes_multipliers[class_id] : 1.0f;
if (l.objectness_smooth) l.delta[class_index + stride*class_id] = class_multiplier * (iou_multiplier - l.output[class_index + stride*class_id]);
box truth = float_to_box_stride(state.truth + best_t*(4 + 1) + b*l.truths, 1);
delta_yolo_box(truth, l.output, l.biases, l.mask[n], box_index, i, j, l.w, l.h, state.net.w, state.net.h, l.delta, (2 - truth.w*truth.h), l.w*l.h, l.iou_normalizer * class_multiplier, l.iou_loss, 1, l.max_delta);
}
}
}
}
for (t = 0; t < l.max_boxes; ++t) { // 遍历每一个GT box。
box truth = float_to_box_stride(state.truth + t*(4 + 1) + b*l.truths, 1); // 将第t个b-box由float数组转b-box结构体,方便计算IOU。
if (truth.x < 0 || truth.y < 0 || truth.x > 1 || truth.y > 1 || truth.w < 0 || truth.h < 0) {
char buff[256];
printf(" Wrong label: truth.x = %f, truth.y = %f, truth.w = %f, truth.h = %f \n", truth.x, truth.y, truth.w, truth.h);
sprintf(buff, "echo \"Wrong label: truth.x = %f, truth.y = %f, truth.w = %f, truth.h = %f\" >> bad_label.list",
truth.x, truth.y, truth.w, truth.h);
system(buff);
}
int class_id = state.truth[t*(4 + 1) + b*l.truths + 4];
if (class_id >= l.classes || class_id < 0) continue; // if label contains class_id more than number of classes in the cfg-file and class_id check garbage value
if (!truth.x) break; // 如果x坐标为0则取消,定义了max_boxes个bbox,可能实际上没那么多。
float best_iou = 0; // 保存最大的IOU。
int best_n = 0; // 保存最大IOU的b-box index。
i = (truth.x * l.w); // 获得当前t个GT b-box所在的cell。
j = (truth.y * l.h);
box truth_shift = truth;
truth_shift.x = truth_shift.y = 0; // 将truth_shift的box位置移动到0,0。
for (n = 0; n < l.total; ++n) { // 遍历每一个anchor b-box找到与GT b-box最大的IOU。
box pred = { 0 };
pred.w = l.biases[2 * n] / state.net.w; // 计算pred b-box的w在相对整张输入图片的位置。
pred.h = l.biases[2 * n + 1] / state.net.h; // 计算pred bbox的h在相对整张输入图片的位置。
float iou = box_iou(pred, truth_shift); // 计算GT box truth_shift与预测b-box pred二者之间的IOU。
if (iou > best_iou) {
best_iou = iou; // 记录最大的IOU。
best_n = n; // 记录该b-box的编号n。
}
}
int mask_n = int_index(l.mask, best_n, l.n); // 上面记录b-box的编号,是否由该层Anchor预测的。
if (mask_n >= 0) {
int class_id = state.truth[t*(4 + 1) + b*l.truths + 4];
if (l.map) class_id = l.map[class_id];
int box_index = entry_index(l, b, mask_n*l.w*l.h + j*l.w + i, 0); // 获得best_iou对应anchor box的index。
const float class_multiplier = (l.classes_multipliers) ? l.classes_multipliers[class_id] : 1.0f; // 控制样本数量不均衡,即Focal Loss中的alpha。
ious all_ious = delta_yolo_box(truth, l.output, l.biases, best_n, box_index, i, j, l.w, l.h, state.net.w, state.net.h, l.delta, (2 - truth.w*truth.h), l.w*l.h, l.iou_normalizer * class_multiplier, l.iou_loss, 1, l.max_delta); // 计算best_iou对应Anchor bbox的[x,y,w,h]的梯度。
/* 模板检测最新的工作,metricl learning,包括IOU/GIOU/DIOU/CIOU Loss等。*/
// range is 0 <= 1
tot_iou += all_ious.iou;
tot_iou_loss += 1 - all_ious.iou;
// range is -1 <= giou <= 1
tot_giou += all_ious.giou;
tot_giou_loss += 1 - all_ious.giou;
tot_diou += all_ious.diou;
tot_diou_loss += 1 - all_ious.diou;
tot_ciou += all_ious.ciou;
tot_ciou_loss += 1 - all_ious.ciou;
int obj_index = entry_index(l, b, mask_n*l.w*l.h + j*l.w + i, 4); // 获得best_iou对应anchor box的confidence的index。
avg_obj += l.output[obj_index]; // 统计confidence。
l.delta[obj_index] = class_multiplier * l.cls_normalizer * (1 - l.output[obj_index]); // 计算confidence的梯度。
int class_index = entry_index(l, b, mask_n*l.w*l.h + j*l.w + i, 4 + 1); // 获得best_iou对应GT box的class的index。
delta_yolo_class(l.output, l.delta, class_index, class_id, l.classes, l.w*l.h, &avg_cat, l.focal_loss, l.label_smooth_eps, l.classes_multipliers); // 获得best_iou对应anchor box的class的index。
++count;
++class_count;
if (all_ious.iou > .5) recall += 1;
if (all_ious.iou > .75) recall75 += 1;
}
// iou_thresh
for (n = 0; n < l.total; ++n) {
int mask_n = int_index(l.mask, n, l.n);
if (mask_n >= 0 && n != best_n && l.iou_thresh < 1.0f) {
box pred = { 0 };
pred.w = l.biases[2 * n] / state.net.w;
pred.h = l.biases[2 * n + 1] / state.net.h;
float iou = box_iou_kind(pred, truth_shift, l.iou_thresh_kind); // IOU, GIOU, MSE, DIOU, CIOU
// iou, n
if (iou > l.iou_thresh) {
int class_id = state.truth[t*(4 + 1) + b*l.truths + 4];
if (l.map) class_id = l.map[class_id];
int box_index = entry_index(l, b, mask_n*l.w*l.h + j*l.w + i, 0);
const float class_multiplier = (l.classes_multipliers) ? l.classes_multipliers[class_id] : 1.0f;
ious all_ious = delta_yolo_box(truth, l.output, l.biases, n, box_index, i, j, l.w, l.h, state.net.w, state.net.h, l.delta, (2 - truth.w*truth.h), l.w*l.h, l.iou_normalizer * class_multiplier, l.iou_loss, 1, l.max_delta);
// range is 0 <= 1
tot_iou += all_ious.iou;
tot_iou_loss += 1 - all_ious.iou;
// range is -1 <= giou <= 1
tot_giou += all_ious.giou;
tot_giou_loss += 1 - all_ious.giou;
tot_diou += all_ious.diou;
tot_diou_loss += 1 - all_ious.diou;
tot_ciou += all_ious.ciou;
tot_ciou_loss += 1 - all_ious.ciou;
int obj_index = entry_index(l, b, mask_n*l.w*l.h + j*l.w + i, 4);
avg_obj += l.output[obj_index];
l.delta[obj_index] = class_multiplier * l.cls_normalizer * (1 - l.output[obj_index]);
int class_index = entry_index(l, b, mask_n*l.w*l.h + j*l.w + i, 4 + 1);
delta_yolo_class(l.output, l.delta, class_index, class_id, l.classes, l.w*l.h, &avg_cat, l.focal_loss, l.label_smooth_eps, l.classes_multipliers);
++count;
++class_count;
if (all_ious.iou > .5) recall += 1;
if (all_ious.iou > .75) recall75 += 1;
}
}
}
}
// averages the deltas obtained by the function: delta_yolo_box()_accumulate
for (j = 0; j < l.h; ++j) {
for (i = 0; i < l.w; ++i) {
for (n = 0; n < l.n; ++n) {
int box_index = entry_index(l, b, n*l.w*l.h + j*l.w + i, 0); // 获得第j*w+i个cell第n个b-box的index。
int class_index = entry_index(l, b, n*l.w*l.h + j*l.w + i, 4 + 1); // 获得第j*w+i个cell第n个b-box的类别。
const int stride = l.w*l.h; // 特征图的大小。
averages_yolo_deltas(class_index, box_index, stride, l.classes, l.delta); // 对梯度进行平均。
}
}
}
}
......
// gIOU loss + MSE (objectness) loss
if (l.iou_loss == MSE) {
*(l.cost) = pow(mag_array(l.delta, l.outputs * l.batch), 2);
}
else {
// Always compute classification loss both for iou + cls loss and for logging with mse loss
// TODO: remove IOU loss fields before computing MSE on class
// probably split into two arrays
if (l.iou_loss == GIOU) {
avg_iou_loss = count > 0 ? l.iou_normalizer * (tot_giou_loss / count) : 0; // 平均IOU损失,参考上面代码,tot_iou_loss += 1 – all_ious.iou。
}
else {
avg_iou_loss = count > 0 ? l.iou_normalizer * (tot_iou_loss / count) : 0; // 平均IOU损失,参考上面代码,tot_iou_loss += 1 – all_ious.iou。
}
*(l.cost) = avg_iou_loss + classification_loss; // Loss值传递给l.cost,IOU与分类损失求和。
}
loss /= l.batch; // 平均Loss。
classification_loss /= l.batch;
iou_loss /= l.batch;
……
}
再来分析backward_network()函数:
void backward_network(network net, network_state state)
{
int i;
float *original_input = state.input;
float *original_delta = state.delta;
state.workspace = net.workspace;
for(i = net.n-1; i >= 0; –i){
state.index = i;
if(i == 0){
state.input = original_input;
state.delta = original_delta;
}else{
layer prev = net.layers[i-1];
state.input = prev.output;
state.delta = prev.delta; // delta是指针变量,对state.delta做修改,就相当与对prev层的delta做了修改。
}
layer l = net.layers[i];
if (l.stopbackward) break;
if (l.onlyforward) continue;
l.backward(l, state); // 不同层l.backward代表不同函数,如:convolutional_layer.c中,l.backward = backward_convolutional_layer;yolo_layer.c中,l.backward = backward_yolo_layer,CPU执行反向传播。
}
}
卷积层时,backward_convolutional_layer()函数:
void backward_convolutional_layer(convolutional_layer l, network_state state)
{
int i, j;
/* m是卷积核的个数,k是每个卷积核的参数数量(l.size是卷积核的大小),n是每个输出feature map的像素个数。*/
int m = l.n / l.groups;
int n = l.size*l.size*l.c / l.groups;
int k = l.out_w*l.out_h;
/* 更新delta。*/
if (l.activation == SWISH) gradient_array_swish(l.output, l.outputs*l.batch, l.activation_input, l.delta);
else if (l.activation == MISH) gradient_array_mish(l.outputs*l.batch, l.activation_input, l.delta);
else if (l.activation == NORM_CHAN_SOFTMAX || l.activation == NORM_CHAN_SOFTMAX_MAXVAL) gradient_array_normalize_channels_softmax(l.output, l.outputs*l.batch, l.batch, l.out_c, l.out_w*l.out_h, l.delta);
else if (l.activation == NORM_CHAN) gradient_array_normalize_channels(l.output, l.outputs*l.batch, l.batch, l.out_c, l.out_w*l.out_h, l.delta);
else gradient_array(l.output, l.outputs*l.batch, l.activation, l.delta);
if (l.batch_normalize) { // BN层,加速收敛。
backward_batchnorm_layer(l, state);
}
else { // 直接加上bias。
backward_bias(l.bias_updates, l.delta, l.batch, l.n, k);
}
for (i = 0; i < l.batch; ++i) {
for (j = 0; j < l.groups; ++j) {
float *a = l.delta + (i*l.groups + j)*m*k;
float *b = state.workspace;
float *c = l.weight_updates + j*l.nweights / l.groups;
/* 进入本函数之前,在backward_network()函数中,已经将net.input赋值为prev.output,若当前层为第l层,则net.input为第l-1层的output。*/
float *im = state.input + (i*l.groups + j)* (l.c / l.groups)*l.h*l.w;
im2col_cpu_ext(
im, // input
l.c / l.groups, // input channels
l.h, l.w, // input size (h, w)
l.size, l.size, // kernel size (h, w)
l.pad * l.dilation, l.pad * l.dilation, // padding (h, w)
l.stride_y, l.stride_x, // stride (h, w)
l.dilation, l.dilation, // dilation (h, w)
b); // output
gemm(0, 1, m, n, k, 1, a, k, b, k, 1, c, n); // 计算当前层weights更新。
/* 计算上一层的delta,进入本函数之前,在backward_network()函数中,已经将net.delta赋值为prev.delta,若当前层为第l层,则net.delta为第l-1层的delta。*/
if (state.delta) {
a = l.weights + j*l.nweights / l.groups;
b = l.delta + (i*l.groups + j)*m*k;
c = state.workspace;
gemm(1, 0, n, k, m, 1, a, n, b, k, 0, c, k);
col2im_cpu_ext(
state.workspace, // input
l.c / l.groups, // input channels (h, w)
l.h, l.w, // input size (h, w)
l.size, l.size, // kernel size (h, w)
l.pad * l.dilation, l.pad * l.dilation, // padding (h, w)
l.stride_y, l.stride_x, // stride (h, w)
l.dilation, l.dilation, // dilation (h, w)
state.delta + (i*l.groups + j)* (l.c / l.groups)*l.h*l.w); // output (delta)
}
}
}
}
yolo层时,backward_yolo_layer()函数:
void backward_yolo_layer(const layer l, network_state state)
{
axpy_cpu(l.batch*l.inputs, 1, l.delta, 1, state.delta, 1); // 直接把l.delta拷贝给上一层的delta。注意 net.delta 指向 prev_layer.delta。
}
正向、反向传播后,通过get_network_cost()函数计算Loss:
float get_network_cost(network net)
{
int i;
float sum = 0;
int count = 0;
for(i = 0; i < net.n; ++i){
if(net.layers[i].cost){ // 获取各层的损失,只有detection层,也就是yolo层,有cost。
sum += net.layers[i].cost[0]; // Loss总和存在cost[0]中,见cost_layer.c中forward_cost_layer()函数。
++count;
}
}
return sum/count; // 返回平均损失。
}
这里用一张图解释下Loss公式:
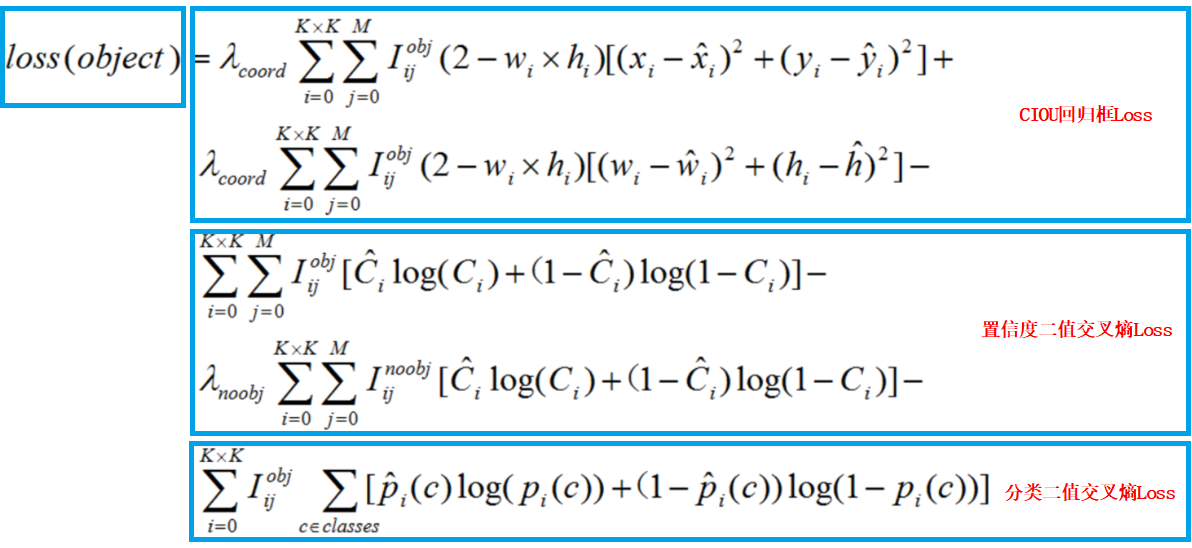
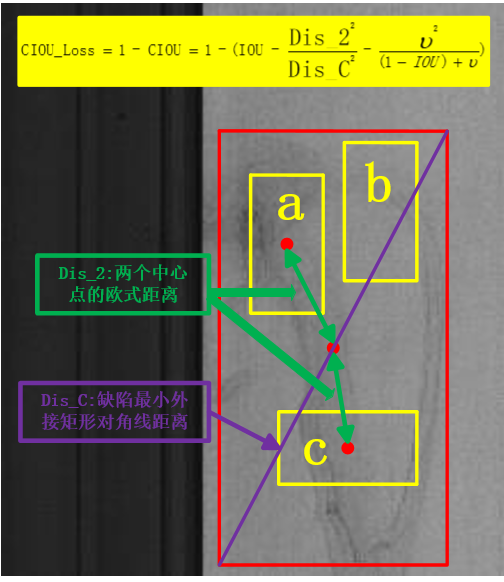
CIOU_Loss是创新点,与GIOU_Loss相比,引入了重叠面积与中心点的距离Dis_2来区分预测框a与b的定位差异,同时还引入了预测框和目标框的长宽比一致性因子ν,将a与c这种重叠面积与中心点距离相同但长宽比与目标框适配程度有差异的预测框区分开来,如图:
计算好Loss需要update_network():
void update_network(network net)
{
int i;
int update_batch = net.batch*net.subdivisions;
float rate = get_current_rate(net);
for(i = 0; i < net.n; ++i){
layer l = net.layers[i];
if(l.update){
l.update(l, update_batch, rate, net.momentum, net.decay); // convolutional_layer.c中,l.update = update_convolutional_layer。
}
}
}
update_convolutional_layer()函数:
void update_convolutional_layer(convolutional_layer l, int batch, float learning_rate_init, float momentum, float decay)
{
float learning_rate = learning_rate_init*l.learning_rate_scale;
axpy_cpu(l.nweights, -decay*batch, l.weights, 1, l.weight_updates, 1); // blas.c中,axpy_cpu函数入口,for(i = 0; i < l.nweights; ++i),l.weight_updates[i*1] -= decay*batch*l.weights[i*1]。
axpy_cpu(l.nweights, learning_rate / batch, l.weight_updates, 1, l.weights, 1); // for(i = 0; i < l.nweights; ++i),l.weights[i*1] += (learning_rate/batch)*l.weight_updates[i*1]
scal_cpu(l.nweights, momentum, l.weight_updates, 1); // blas.c中,scal_cpu函数入口,for(i = 0; i < l.nweights; ++i),l.weight_updates[i*1] *= momentum。
axpy_cpu(l.n, learning_rate / batch, l.bias_updates, 1, l.biases, 1); // for(i = 0; i < l.n; ++i),l.biases[i*1] += (learning_rate/batch)*l.bias_updates[i*1]。
scal_cpu(l.n, momentum, l.bias_updates, 1); // for(i = 0; i < l.n; ++i),l.bias_updates[i*1] *= momentum。
if (l.scales) {
axpy_cpu(l.n, learning_rate / batch, l.scale_updates, 1, l.scales, 1);
scal_cpu(l.n, momentum, l.scale_updates, 1);
}
}
同样,在network_kernels.cu里,有GPU模式下的forward&backward相关的函数,涉及数据格式转换及加速,此处只讨论原理,暂时忽略GPU部分的代码。
void forward_backward_network_gpu(network net, float *x, float *y)
{
......
forward_network_gpu(net, state); // 正向。
backward_network_gpu(net, state); // 反向。
......
}
CPU模式下,采用带momentum的常规GD更新weights,同时在network.c中也提供了也提供了train_network_sgd()函数接口;GPU模式提供了adam选项,convolutional_layer.c中make_convolutional_layer()函数有体现。
七. 调参总结
本人在实际项目中涉及的是工业中的钢铁表面缺陷检测场景,不到2000张图片,3类,数据量很少。理论上YOLO系列并不太适合缺陷检测的问题,基于分割+分类的网络、Cascade-RCNN等或许是更好的选择,但我本着实验的态度,进行了多轮的训练和对比,整体上效果还是不错的。
1.max_batches: AlexeyAB在github工程上有提到,类别数*2000作为参考,不要少于6000,但这个是使用预训练权重的情况。如果train from scratch,要适当增加,具体要看你的数据情况,网络需要额外的时间来从零开始学习;
2.pretrain or not:当数据量很少时,预训练确实能更快使模型收敛,效果也不错,但缺陷检测这类问题,缺陷目标特征本身的特异性还是比较强的,虽然我的数据量也很少,但scratch的方式还是能取得稍好一些的效果;
3.anchors:cfg文件默认的anchors是基于COCO数据集,可以说尺度比较均衡,使用它效果不会差,但如果你自己的数据在尺度分布上不太均衡,建议自行生成新的anchors,可以直接使用源码里面的脚本,注意,要根据生成anchors的size(1-yolo:<30*30,2-yolo:<60*60,3-yolo:others)来改变索引值masks以及前一个conv层的filters参数;
4.rotate:YOLO-V4在目标检测这一块,其实没有用到旋转来进行数据增强,因此我在线下对数量最少的一个类进行了180旋转对称增强,该类样本数扩增一倍,效果目前还不明显,可能是数据量增加的还是太少,而且我还在训练对比,完成后可以补充;
5.mosaic:马赛克数据增强是必须要有的,mAP值提升比较明显,需要安装opencv,且和cutmix不能同时使用。
 Mikel
Mikel


